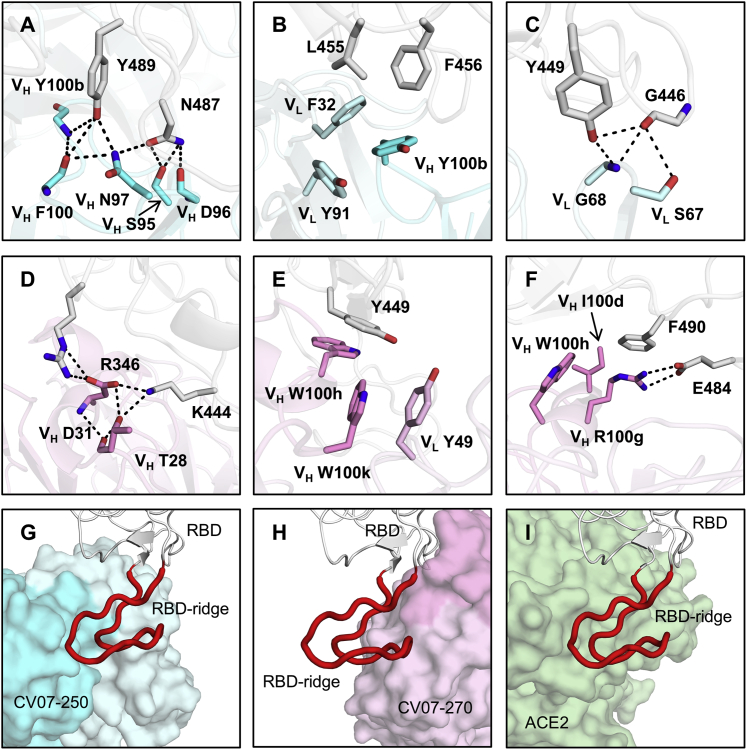
Figure 4.
Interactions and Angle of Approach at the RBD-Antibody Interface
(A–C) Key interactions between CV07-250 (cyan) and the RBD (white) are highlighted.
(A) CDR H3 of CV07-250 forms a hydrogen bond network with RBD Y489 and N487.
(B) VH Y100b (CDR H3), VL F32 (CDR L1), and VL Y91 (CDR L3) of CV07-250 form a hydrophobic aromatic patch for interaction with RBD L455 and F456.
(C) The side chain of VL S67 and backbone amide of VL G68 from FR3 are engaged in a hydrogen bond network with RBD G446 and Y449.
(D–F) Interactions between CV07-270 (cyan) and the RBD (white).
(D) Residues in CDR H1 of CV07-270 participate in an electrostatic and hydrogen bond network with RBD R346 and K444.
(E) VH W100h and VH W100k on CDR H3 of CV07-270 make π-π stacking interactions with Y449. VH W100k is also stabilized by a π-π stacking interaction with VL Y49.
(F) VH R100 g on CDR H3 of CV07-270 forms an electrostatic interaction with RBD E484 as well as a π-cation interaction with RBD F490. Oxygen atoms are shown in red and nitrogen atoms in blue. Hydrogen bonds are represented by dashed lines.
(G–I) Magnified views of the different RBD ridge interactions with (G) CV07-250, (H) CV07-270, and (I) ACE2 (PDB: 6M0J; Lan et al., 2020). The ACE2-binding ridge in the RBD is represented by a backbone ribbon trace in red.
See also Figures S5 and S6 and Tables S4 and S5.