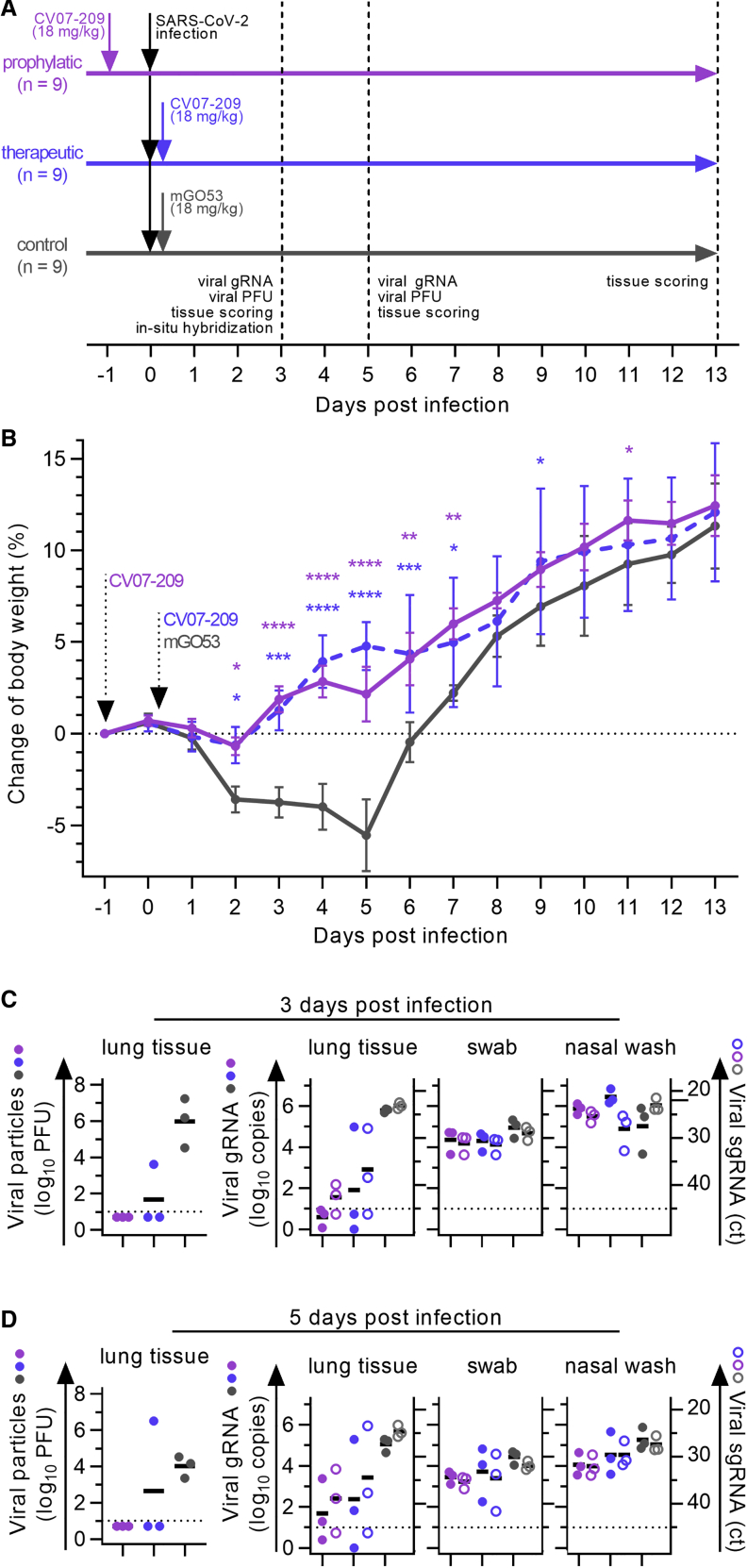
Figure 5.
Prophylactic and Therapeutic Application of mAb CV07-209 in a COVID-19 Hamster Model
(A) Schematic overview of the animal experiment.
(B) Body weight of hamsters after virus challenge and prophylactic (pink) or therapeutic (blue) application of the SARS-CoV-2-neutralizing mAb CV07-209 or control antibody (mean ± SEM from 9 animals per group from days −1 to 3, n = 6 from days 4–5; n = 3 from days 6–13; mixed-effects model with post hoc Dunnett’s multiple tests in comparison with the control group; significance levels are shown as ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 or not shown when not significant.
(C and D) Left: quantification of plaque-forming units (PFU) from lung homogenates. Right: quantification of genomic SARS-CoV-2 RNA (gRNA) as copies per 105 cellular transcripts (left y axis, filled circles) and cycle threshold (ct) of subgenomic SARS-CoV-2 RNA (sgRNA) detection (right y axis, unfilled circles) from samples and time points as indicated. Values for PFUs were set to 5 when not detected, gRNA copies below 1 were set to 1, and the ct of sgRNA was set to 46 when not detected. Bars indicate the mean. Dotted lines represent the detection threshold.