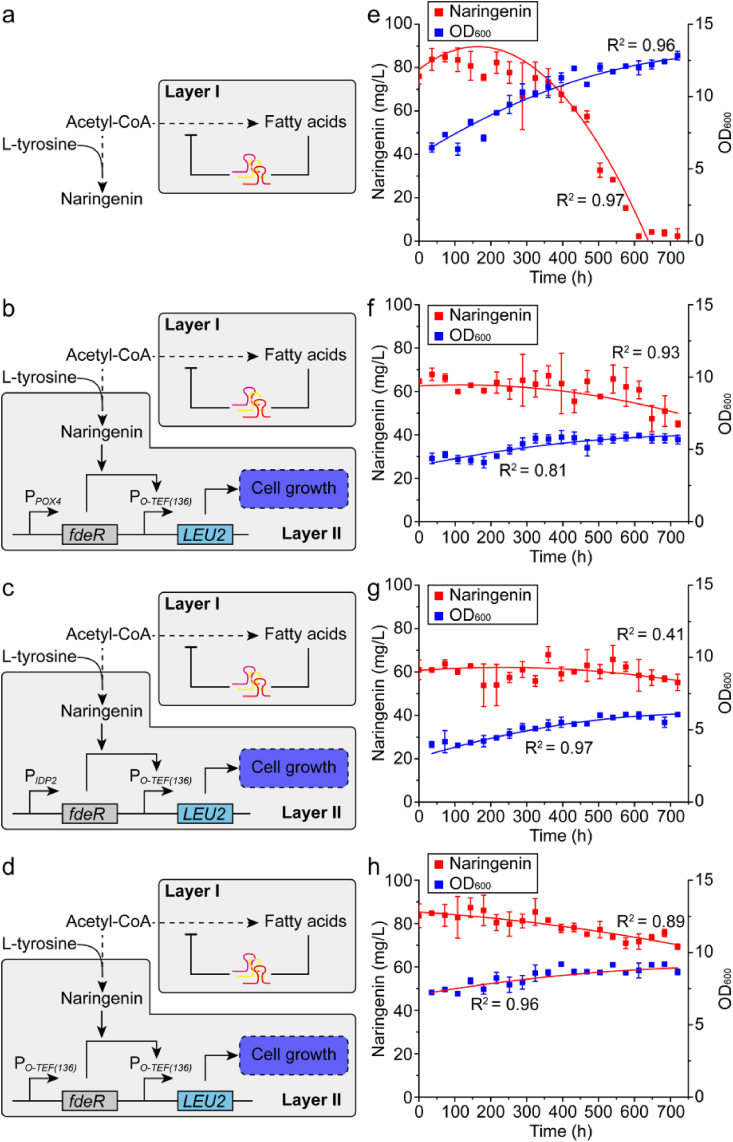
Fig. 7.
Stability analysis of naringenin producing strains equipped with or without naringenin-addiction circuits. The metabolic addiction were coupled with fatty acid negative autoregulation by equipping naringenin addiction circuits (PO-TEF(136)-LEU2-PPOX4-FdeR, PO-TEF(136)-LEU2-PIDP2-FdeR, and PO-TEF(136)-LEU2-PO-TEF(136)-FdeR) to the NarPro/ACS_Rep chassis, which is a naringenin producing strain with fatty acid negative autoregulatory circuit. a. Stability analysis of the control strain (NarPro/ACS_Rep chassis with blank pYLXP′ plasmid). b. Stability analysis of NarPro/ACS_Rep equipped with PO-TEF(136)-LEU2-PPOX4-FdeR. c. Stability analysis of NarPro/ACS_Rep equipped with PO-TEF(136)-LEU2-PIDP2-FdeR. d. Stability analysis of NarPro/ACS_Rep equipped with PO-TEF(136)-LEU2-PO-TEF(136)-FdeR. Long-term fermentation was carried out in CMS-leu synthetic drop out medium. The strains were passaged at exponential phase (every 36 h). Before every passaging, OD600 was measured and samples were taken for frozen stocks. To analyze the naringenin production, the frozen stocks of each sample were re-inoculated into CSM-leu synthetic drop out medium (4% (v/v)). Naringenin titer was measured at 120 h. The lines were the polynomial fits to the means.