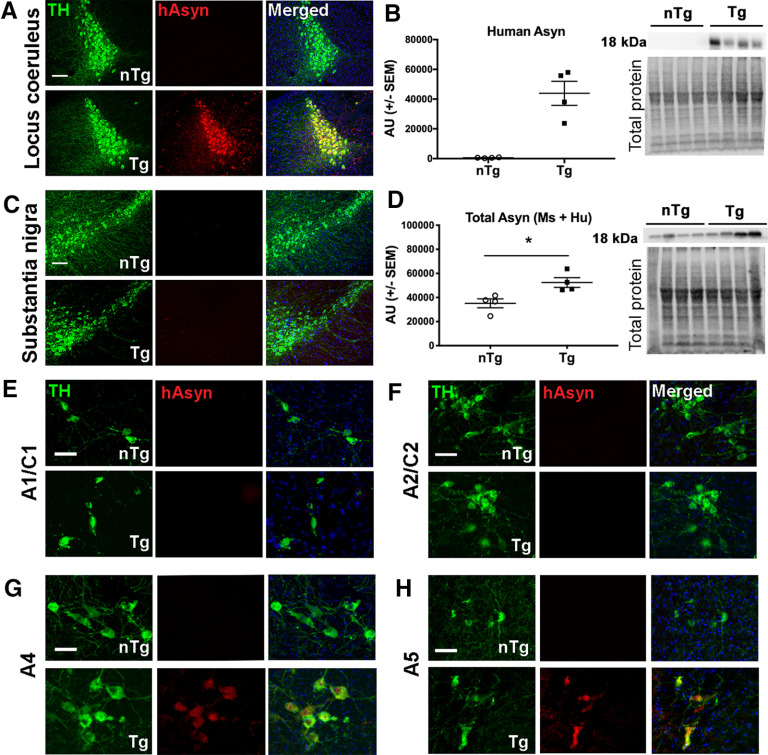
Figure 2.
Analysis of asyn expression in catecholaminergic brainstem regions of young DBH-hSNCA mice. A, C, Immunofluorescent detection of human asyn (hAsyn; red) with a species-specific antibody (catalog #807801, BioLegend) demonstrates colocalization with TH-expressing LC neurons (green) in Tg mice (bottom; A) but not in nTg mice (top) or in TH-expressing neurons (green) in the substantia nigra regardless of genotype (C). B, Human asyn protein is expressed selectively in LC neurons of DBH-hSNCA × TH-EGFP mice by Western blot. D, Immunoblot of LC protein with an antibody against asyn that detects the mouse and human protein reveals a significant increase in total asyn protein expression in LC neurons of DBH-hSNCA × TH-EGFP mice compared with that in LC of nTg littermate mice. Immunoblot data graphed as arbitrary units (AU) normalized to total protein. E–H, Human asyn is not expressed in the A1/C1 (E) or the A2/C2 region (F), but is detectable in the A4 (G) and A5 (H) regions of Tg mice by immunofluorescence. All data are from 3-month-old nTg and Tg mice. Scale bars: A, C, 100 µm; E–H, 50 µm. Student's t test ± SEM, *p < 0.05.