Figure 1.
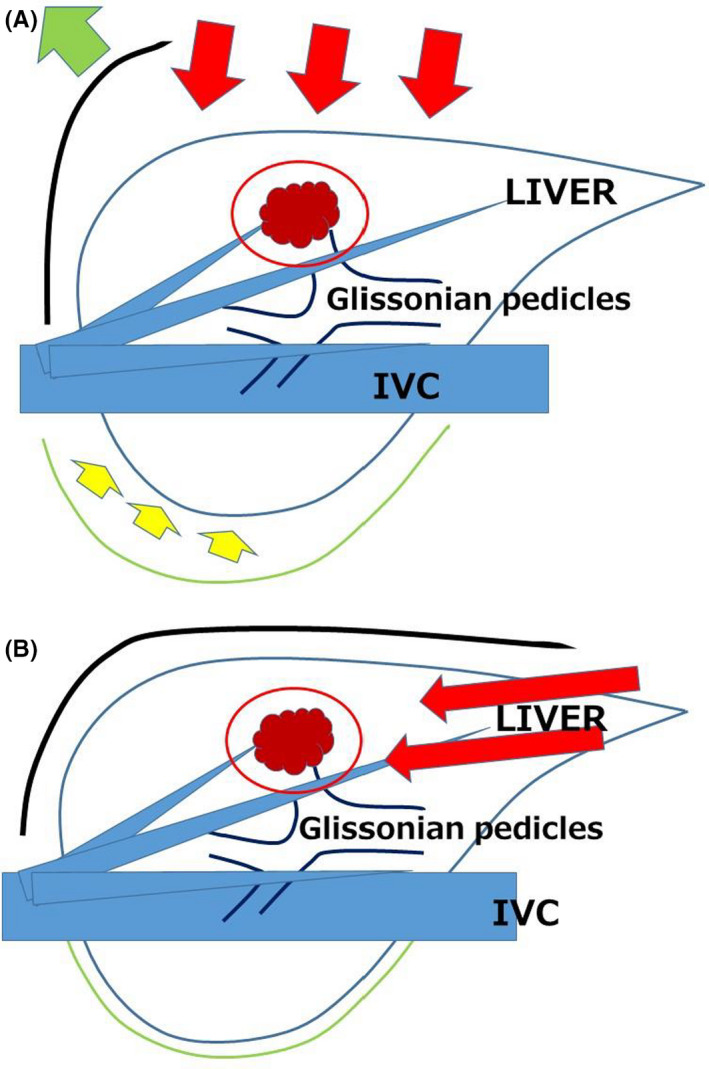
Schema of open liver resection (A) and laparoscopic liver resection (caudal approach, B). Red arrows indicate the directions of view and manipulation in each approach. A. In the open approach, the subphrenic rib cage containing the liver is opened with a large subcostal incision and instruments are used to lift the costal arch up, and the liver is dissected and mobilized (lifted) from the retroperitoneum; B, In laparoscopic caudal approach, the laparoscope and forceps intrude into the subphrenic rib cage from the caudal direction, and the surgery is performed with minimal alteration and destruction of the associated structures. In the same context, direct approach to the tumor in LRLR after minimal adhesiolysis for the surgical space can be facilitated especially in small LRLR. (Modification from Morise Z, Wakabayashi G. First quarter century of laparoscopic liver resection. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(20):3581‐3588. 8 )
