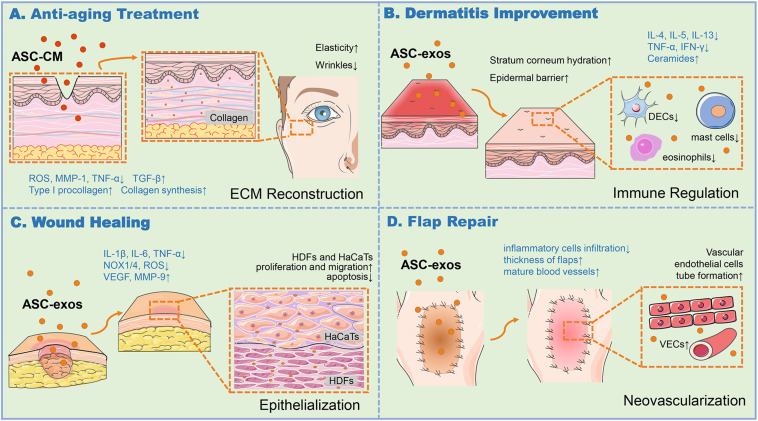
FIGURE 1.
ASC-exos function in various skin associated applications. (A) ASC-CM and BMSC-exos could produce ROS at a low level, downregulate TNF-α, upregulate TGF-β to increase MMP-1 and procollagen type I expression for collagen synthesis, thus enhancing the skin elasticity and ease the wrinkles for anti-aging. (B) ASC-exos was capable to enhance stratum corneum hydration, reduce the secretion of inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IFN-γ, and TNF-α, and alleviate the infiltration of mast cells, dendritic epidermal cells (DECs) in skin lesions and eosinophils in the blood, and produce ceramides to restore the epidermal barrier, thus relieving the dermatitis of skin. (C) ASC-exos reduced the production of ROS, decrease the expression of IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and the oxidative stress-related proteins such as NADPH oxidase 1/4 (NOX1/4), increase MMP-9 and VEGF to ameliorate ECM reconstruction, thus fostering HDFs proliferation and migration to reinforce the re-epithelialization. (D) ASC-exos was conducive to promote tube formation of VECs, increase tissue thickness, and reduce the infiltration of inflammatory cells to relieve the inflammation and apoptosis for the high survival rate of the skin flap. ASCs, Adipose-derived stem cells; ASC-exos, ASC-derived exosomes; HDFs, Human Dermal Fibroblasts; HaCaTs, Human Keratinocytes; ECM, Extracellular Matrix; ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; MMP-1/9, Matrix Metalloproteinase 1/9; IFN-γ, Interferon Gamma; TNF-α, Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha; TGF-β, Transforming Growth Factor Beta; IL-4/5/6/13, Interleukin 4/5/6/13; NOX-1/4, NADPH Oxidase 1/4; VEGF, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor; VECs, Vascular Endothelial Cells, VECs.