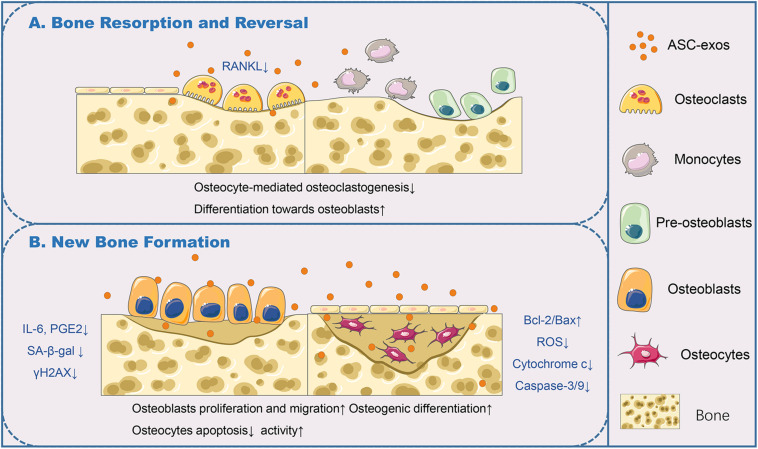
FIGURE 2.
ASC-exos function in the bone remodeling cycle. (A) In bone resorption and reversal, ASC-exos could decrease the expression of RANKL, which was highly expressed by osteoclasts or their precursors for osteoclast activation, to antagonize osteocyte-mediated osteoclastogenesis. (B) In bone formation, ASC-exos possessed the ability of lowering the production of IL-6 and PGE2, downregulating SA-β-gal activity and reducing the accumulation of γH2AX in osteoblasts. Additionally, ASC-exos could upregulate the radio of Bcl-2/Bax, diminish the production of ROS and cytochrome c, and subsequent activation of caspase-3/9 in osteocytes. ASCs, Adipose-derived stem cells; ASC-exos, ASC-derived exosomes; RANKL, Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor Kappa B Ligand; IL-6, Interleukin 6; PGE2, Prostaglandin E2; SA-β-gal, Senescence-Associated β-galactosidase; γH2AX, Phosphorylated Histone H2AX; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; Caspase-3/9, Aspartate Proteolytic Enzyme 3/9.