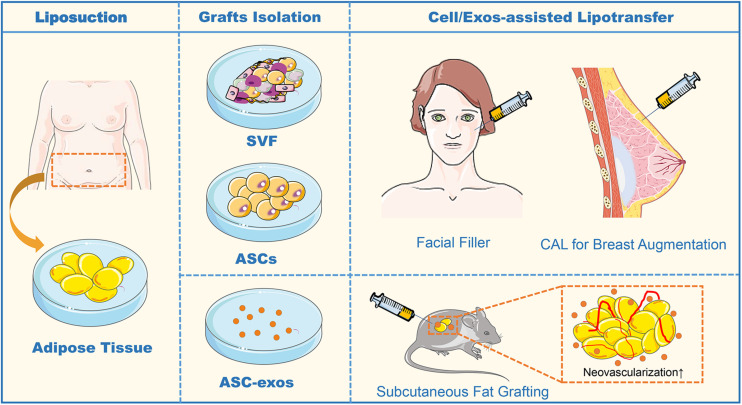
FIGURE 4.
The sequence flow diagram of fat grafting. In the clinical application of fat grafting for facial filler and breast augmentation, sterile adipose tissue is collected through liposuction. After enzyme digestion and centrifugation of the collected adipose tissue, the obtained heterogeneous mixture of endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, fibroblast, pericytes, mast cells, and preadipocytes is named SVF. In CAL, half the volume of the aspirated fat is processed for isolation of the SVF containing ASCs, and the other half of the aspirated fat is prepared for grafting. Finally, the SVF-supplemented fat is injected into the target sites of grafting. In animal studies of the subcutaneous fat grafting, co-transplantation of ASC-exos with adipocytes can effectively promote the neovascularization to enhance survival in the fat grafts. ASCs, Adipose-derived stem cells; ASC-exos, ASC-derived exosomes; SVF, Stromal Vascular Fraction; CAL, Cell-Assisted Lipotransfer, CAL.