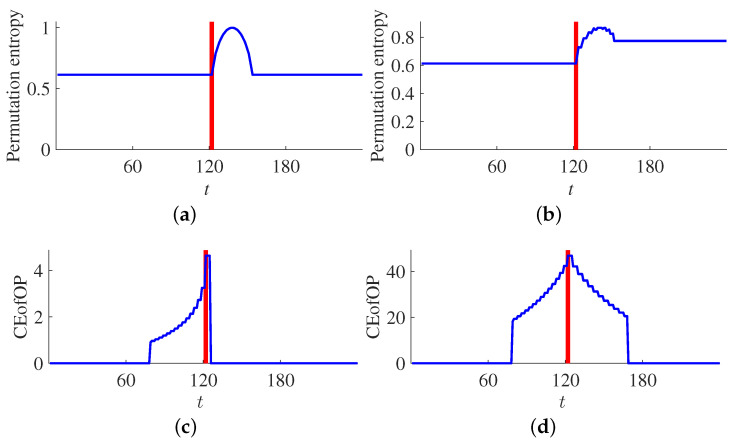
Figure A2.
Permutation entropy computed in sliding windows (a,b) and values of the CEofOP statistics (c,d) for artificial time series with sequences of ordinal patterns and , respectively, where , . Both sequences of ordinal patterns have a change-point at (indicated by red vertical line) and are given by and . Permutation entropy is computed in sliding windows of length . While peaks of the CEofOP statistics clearly indicate the change-points, there is no straightforward way to detect changes from the values of permutation entropy.