Fig. 5.
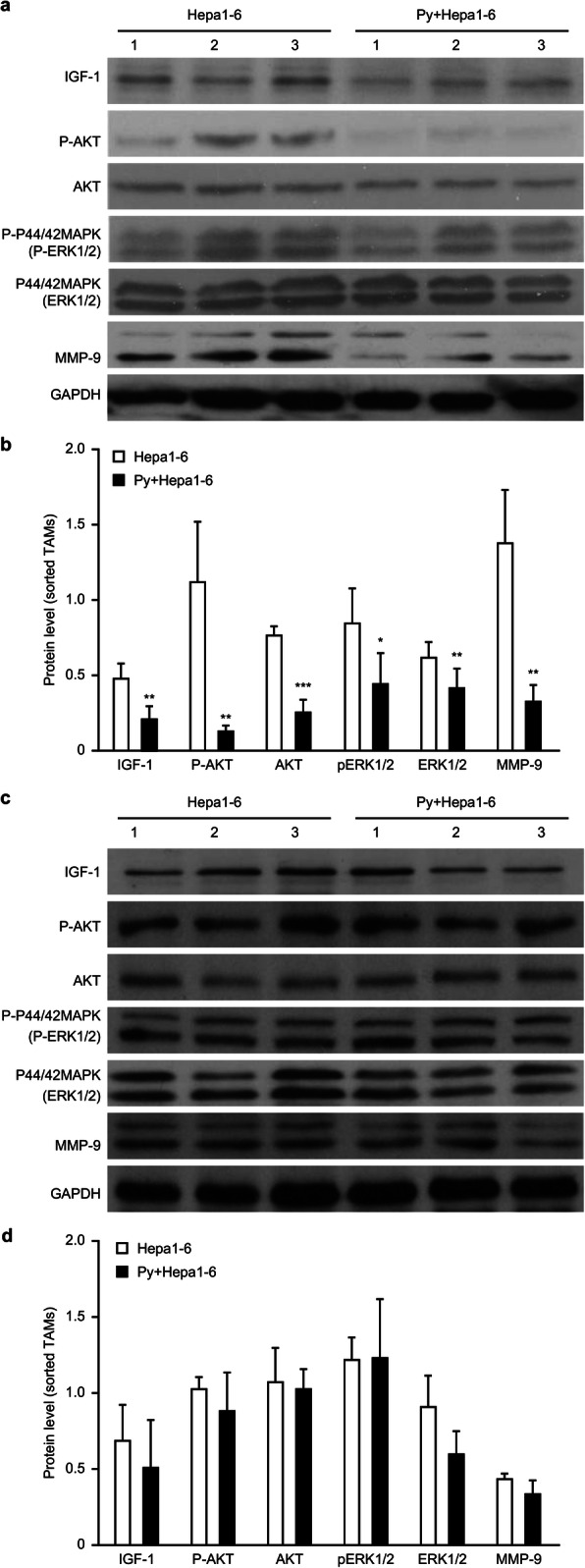
Plasmodium infection attenuated MMP-9 expression by blocking IGF-1R signaling. a-b The expression of IGF-1, MMP-9, phosphorylated Akt, total Akt, phosphorylated p42/44 MAPK and total MAPK in the sorted TAMs from tumor-bearing mice on day 17 after Plasmodium infection was detected by immunoblotting (a). A quantitative analysis was performed using ImageJ software to quantify the levels of these signaling proteins in the sorted TAMs (b). c-d The Plasmodium parasites were killed by chloroquine on day 8, and the AKT and MAPK signaling pathways were examined. A Western blotting assay was performed to visualize the restoration of the levels of these signaling proteins (c). A quantitative analysis of signaling proteins in the sorted TAMs from the tumor-bearing mice with Plasmodium infection blocked on day 8 was performed using ImageJ software (d)
