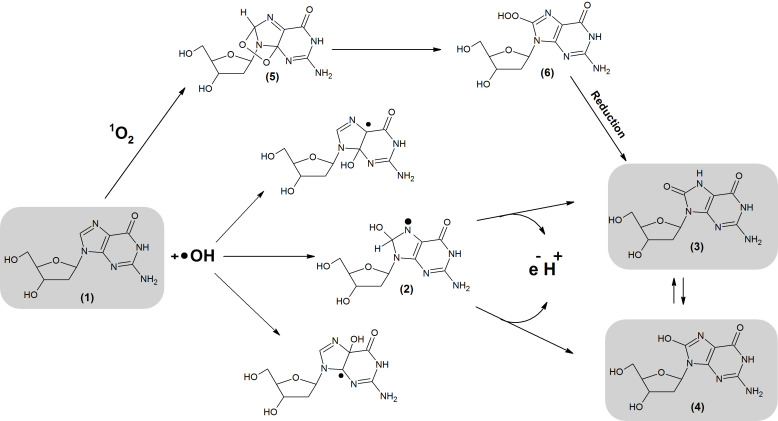
Figure 3.
Formation of 8-oxodG and 8-OHdG. The lesions are generated through interaction between 1O2 or •OH and G or dG. As a result of •OH addition, different radical adducts are formed (1). Subsequently, electron abstraction generates 8-OHdG which undergoes keto-enol tautomerism forming an oxidized product: 8-oxodG. 8-oxodG and 8-OHdG lesions can also be generated by cycloaddition of 1O2 into the imidazole ring of dG. This reaction generates (5) which is later rearranged into (6). (1) 2′-deoxyguanosine, (2) 8-Hydroxy-7,8-dihydro-2′-deoxyguanosyl radical, (3) 8-oxodG, (4) 8-OHdG, (5) 4,8-endoperoxide-2′-deoxyguanosine, (6) 8-hydroperoxy-2′-deoxyguanosie.