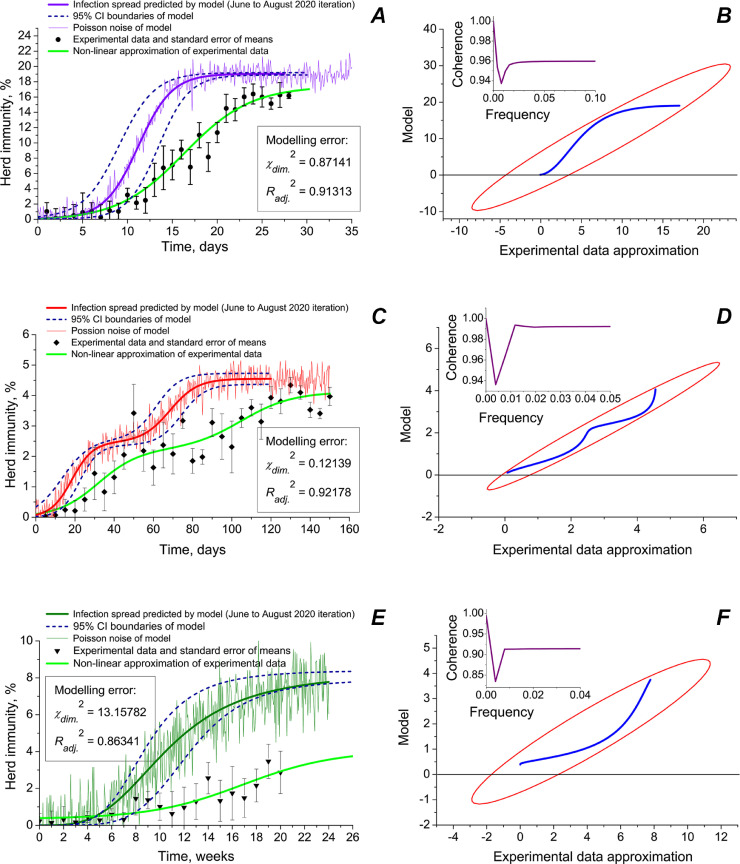
Fig. 6.
Modelling herd immunity, real epidemiological data and statistical treatment of the model for different types of environments: closed communities (A, B), semi-open premises (C, D) and open spaces (E, F). Pearson correlations coefficients between simulated curve and epidemiological data approximation: 0.95882 (p ≤ 0.00183) (A); 0.96290 (p ≤ 0.00072); and 0.93733 (p ≤ 0.01274). In right panes (B, D and F), scatter matrices (blue lines) and 95% correlation CI ellipses (red) are shown. In the insets, coherence vs frequency of signal plots are provided. Coherence between simulated curve and real data is calculated as where Pab the cross power spectral density, and Paa and Pbb are power spectral densities of simulated curve and experimental data means. Estimations of Poisson noise of the model: 5.12% (A); 6.68% (C); and 14.47% (E).