Figure 2.
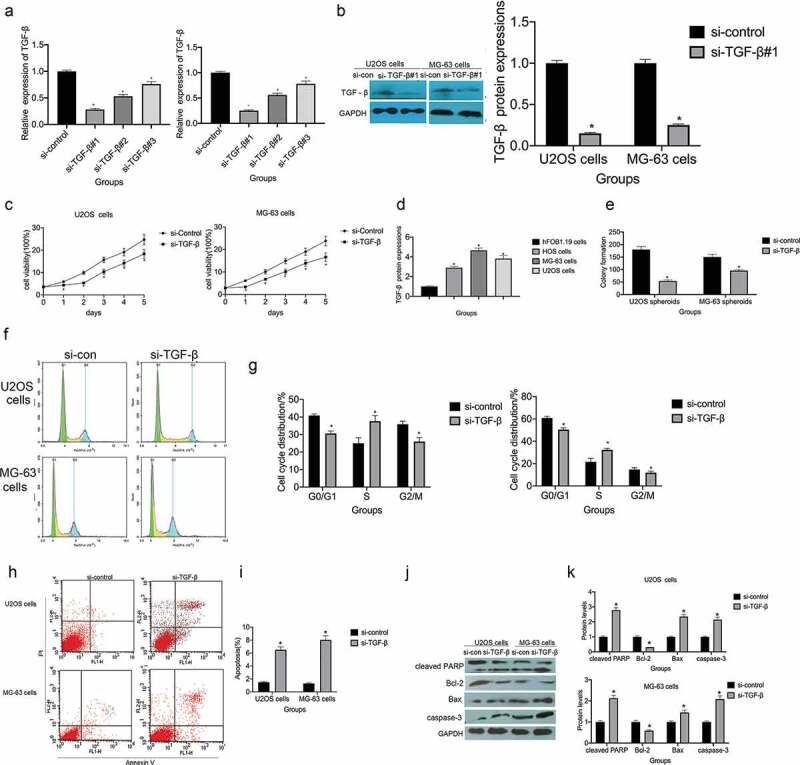
Small interfering (si) RNA targeting of TGF-β (si-TGF-β) suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis in osteosarcoma. (a) RT-qPCR was employed to assess the knockdown efficiency of si-TGF-β, *P < 0.05 vs. the si-control group. (b) Western blotting was used to measure the knockdown efficiency of si-TGF-β, *P < 0.05 vs. the si-control group. (c)The MTT assay was used to assess the viability of U2OS and MG-63 cells transfected with si-control or si-TGF-β, *P < 0.05 vs. the si-control group. (d and e) The colony-forming ability of U2OS and MG-63 cells transfected with si-control or si-TGF -β, *P < 0.05 vs. the si-control group. (f and g) Flow cytometry analysis of the cell cycle phase distribution of U2OS and MG-63 cells transfected with si-control or si-TGF – β, *P < 0.05 vs. the si-control group. (h and i) The rate of apoptosis in U2OS and MG-63 cells transfected with si-TGF-β, *P < 0.05 vs. the si-control group. (j and k) TGF-β knockdown increases the expression of cleaved PARP, caspase-3, and BAX, *P < 0.05 vs. the si-control group.
