Figure 2.
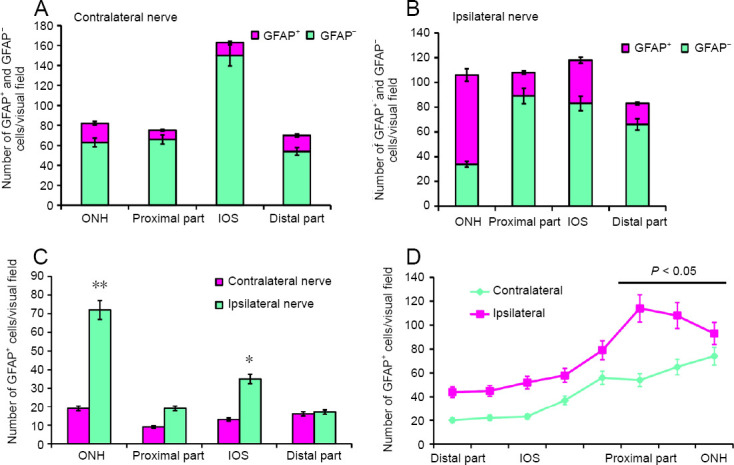
GFAP+ cells and GFAP– cells on the optic nerves of the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, at 1 week after unilateral eye injury.
(A) Number of GFAP+ and GFAP– cells in the ONH, IOS, proximal and distal parts of the contralateral nerve (mean ± SD). (B) Number of GFAP+ and GFAP– cells on the damaged side (mean ± SD). (C) Number of GFAP+ astrocytes in the contralateral and ipsilateral optic nerves; one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test was used to determine significant differences in contralateral and ipsilateral nerves (n = 5 in each group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, vs. contralateral optic nerve). (D) Number of GFAP+ fibers in the contralaeral and ipsilateral optic nerves of the rainbow trout; one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test was used to determine significant differences between contralateral and ipsilateral nerves (n = 5 in each group; *P < 0.05, vs. contralateral optic nerve). GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; IOS: intraorbital segment; ONH: optic nerve head.
