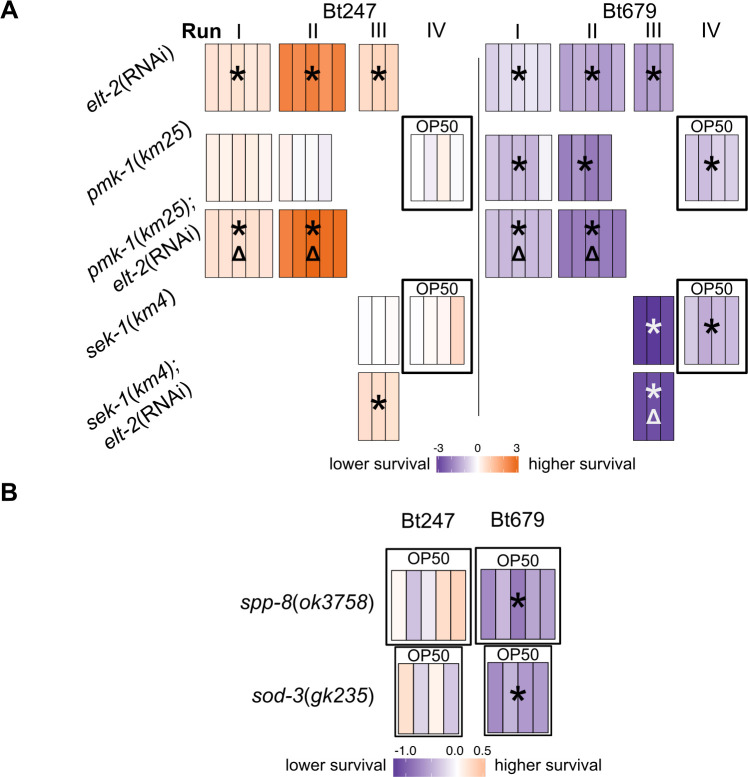
Fig 5. The p38 MAPK pathway and putative effector genes spp-8 and sod-3 are specifically required for defense against Bt679 infection.
Difference in survival at 24 h p.i. between the N2 control and (A) p38 MAPK pmk-1(km25) and MAPKK sek-1(km4) mutant exposed to Bt247 or Bt679, and epistasis analysis following elt-2(RNAi), (B) the putative effector saposin-like protein-encoding gene mutant spp-8(ok3758) and the superoxide dismutase mutant sod-3(gk235). spp-8 and sod-3 are specifically required for resistance against Bt679, but not Bt247. Data represented in heatmaps and statistics as in Fig 3E. Triangles indicate significant difference compared to elt-2(RNAi). In A, worms were grown on RNAi E. coli HT115 plates until L4 larval stage when worms were exposed to Bt. OP50 above a run indicates that the worms were grown on NGM plates seeded with E. coli OP50 (absence of RNAi treatment). See also S3 and S4 Figs.