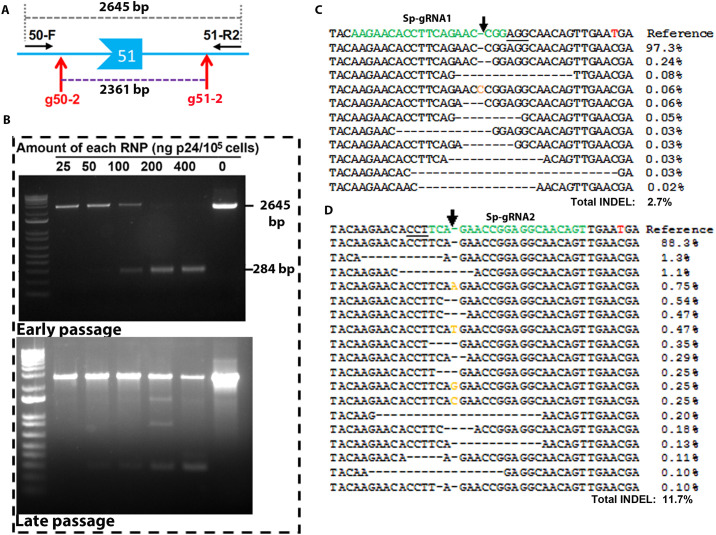
Fig 3. LVLP-RNPs were functional in myoblasts.
A. Cartoon illustrating the location of the gRNAs (g50-2 and g51-2) used for exon 51 removal and the primers (DMD50-F and DMD51-R2) used for PCR detection of exon 51 removal. B. Test the transduction of myoblasts by LVLP-RNPs. Top: efficient removal of exon 51 in early passage hDMDdel52/mdx mouse myoblasts. Indicated amounts of LVLP-RNPs were co-delivered to 105 myoblasts prepared from hDMDdel52/mdx mice. PCR yielded a 2645 bp band if exon 51 was not removed. PCR yielded a 284 bp band if exon 51 was removed. Nearly 100% efficiency of exon 51 removal could be obtained at the doses of 200 ng and 400 ng p24. Bottom: less efficient removal of exon 51 in hDMDdel52/mdx myoblasts by the LVLP-RNPs after the myoblasts had been cultured for one week. See S6 Fig for sequencing data. C. NGS analysis of hDMDdel52/mdx myoblasts gDNA treated with Sp-gRNA1 targeting LVLP-RNPs. D. NGS analysis of hDMDdel52/mdx myoblasts gDNA treated with Sp-gRNA2 targeting LVLP-RNPs. For C and D, the target sequences are in green and the PAM regions are underlined. The brown letters are insertions and the dashes are deletions. The red “T” in the reference sequence is a “C” in hDMDdel52/mdx myoblasts that disrupts the target site for Sa-gRNA2.