Fig. 1.
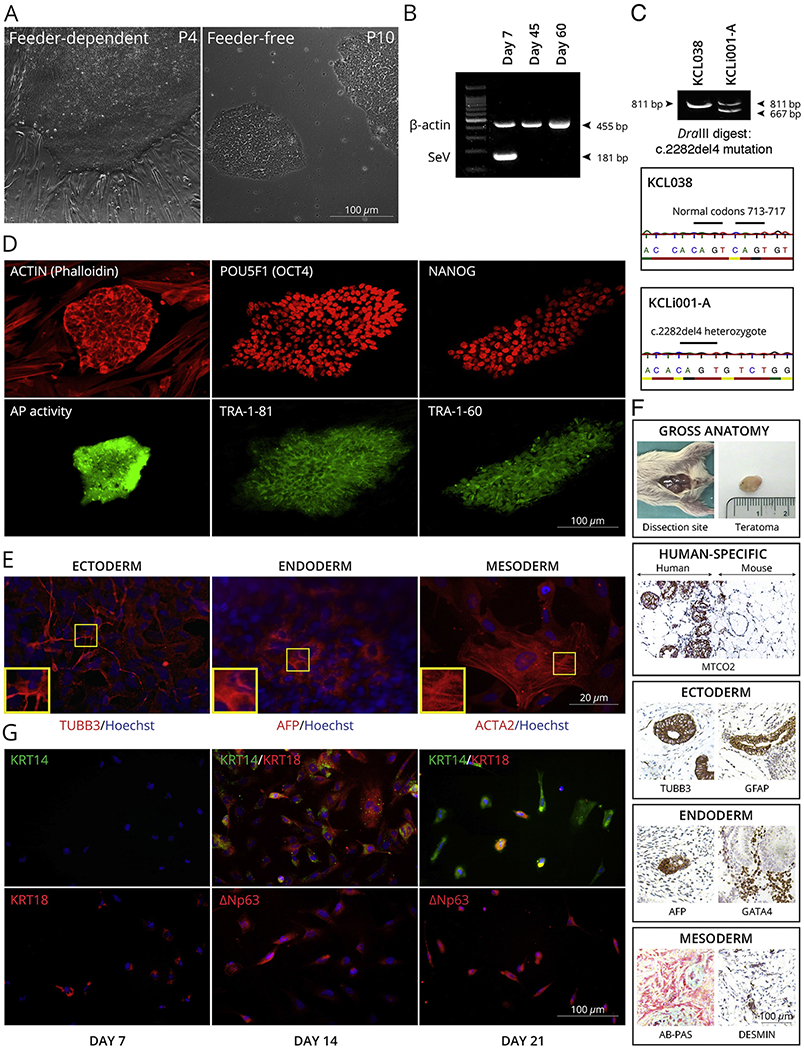
Characterization of KCLi001-A line. A, The colonies display typical morphology of pluripotent stem cells under feeder-dependent and feeder-free conditions. B, The absence of 181 bp positive SeV band at 45 and 60 days of culture indicates that the cells are SeV free. β-actin 455 bp band serves as an internal control. C, The line is heterozygous for c.2282del4 mutation in FLG as indicated with restriction enzyme digestion and Sanger sequencing of PCR product spanning the mutation site. Mutation generates a site for DraIII that is not present in wildtype allele. The enzyme digestion cuts 811 bp product in mutated allele into 667 bp and 134 bp, whereas 811 bp remains intact in wildtype. hESC line KCL038 is used as a negative control. D, Pluripotency markers. Alkaline phosphatase activity (AP) was restricted to the iPSC colony (green) growing on AP-negative feeder cells. Both iPSC colony and feeders are positive for actin (phalloidin) staining (red). iPSC colonies are positive for POU5F1 (red), TRA-1-81 (green), NANOG (red) and TRA-1-60 (green) pluripotency markers. E, Spontaneous differentiation in vitro. The cells can differentiate into all three germ layers as demonstrated with markers specific for ectoderm (TUBB3), endoderm (AFP) and mesoderm (ACTA2). Nuclei are visualized with Hoechst 33342. F, Spontaneous differentiation in vivo. Gross anatomy and staining for human-specific MTCO2 marker iPSC indicated that the teratoma is incapsulated and did not invade surrounding tissues. Teratoma contained cells from all three germ layers as demonstrated with markers specific for ectoderm (TUBB3, GFAP), endoderm (AFP, GATA4) and mesoderm (AB-PAS, DESMIN). G, Directed differentiation into keratinocytes. The cells expressed keratinocyte-specific markers KRT14, KRT18, TP63 (ΔNp63) in time-dependent manner.
