Figure 1.
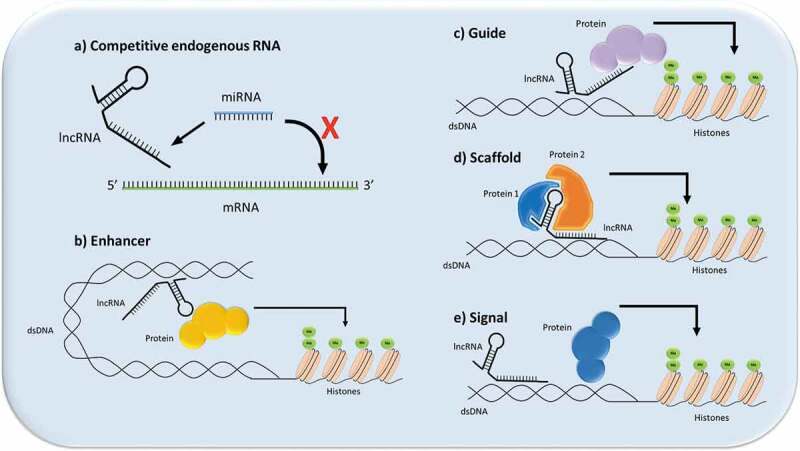
Illustration of the different mechanisms through which lncRNAs can signal. (a) Competitive endogenous RNA function (ceRNA): the lncRNA acts as a functional decoy or “sponge” for other molecules, which prevents the other molecules from executing their function, such as in the case of lncRNA-miRNA sponging; (b) Enhancer function: the lncRNA can act as an enhancer or transcription factor-like molecule in cells to promote gene expression; (c) Guide function: the lncRNA can recruit proteins to a nuclear site,; for instance, to assist in chromatin remodeling; (d) Scaffold function: the lncRNA can act to bring proteins spatially close to each other to aid in ribonuclear protein formation; (e) Signal function: lncRNA acts as a signal for a molecule such as a transcription factor to promote or repress gene expression.
