Figure 1.
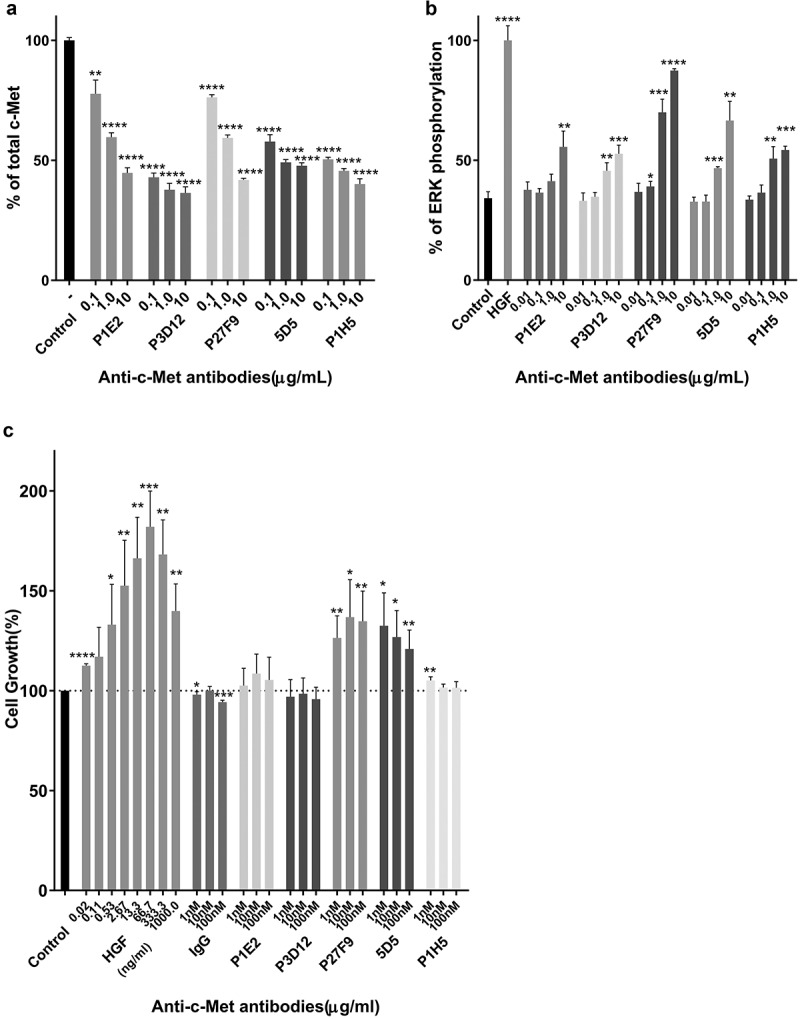
Identification of the lead P3D12 anti-c-Met antibody. cMet antibody candidates were tested for efficient c-Met internalization/degradation, minimal activation (non-agonistic) of the ERK pathway (low phosphorylation) and low cell growth induction (slow cell proliferation).
(a) c-Met degradation in SNU-16 cells was measured with the SECTOR Imager 2400. Cells were treated with anti-c-Met antibodies and incubated for 24 h. Values are plotted as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). % total c-Met; * p < .05, ** p < .01, *** p < .001 and **** p < .0001 compared to control. Significance was determined with student t-test. (b) ERK phosphorylation in MKN-45 cells was measured with the SECTOR Imager 2400. MKN-45 cells were incubated with c-Met antibodies for 15 min. Values are plotted as mean ± S.D. (n = 3). % P-ERK; * p < .05, ** p < .01, *** p < .001 and **** p < .0001 compared to control. Significance was determined with student t-test. (c) c-Met-induced cell proliferation of lead P3D12 cMet antibody. The proliferation of 4MBr-5 cells was measured by CTG assay after treatment with IgG, bivalent 5D5, and anti-c-Met antibodies for 5 days. All groups were normalized to cell growth of the control group (no antibody). Values are generated from three independent experiments with duplicate samples each. Values are plotted as the mean ± S.D. % Cell growth; * p < .05, ** p < .01, *** p < .001 and **** p < .0001 compared to control. Significance was determined with student t-test.
