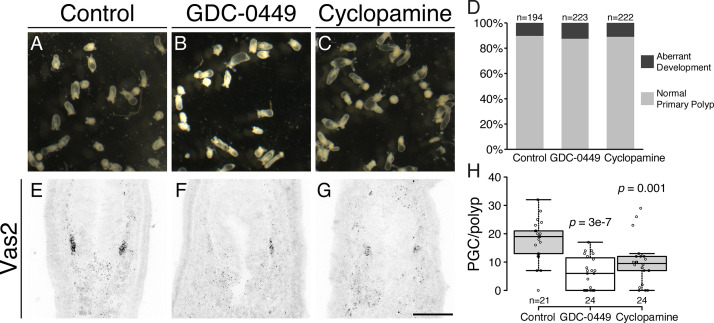
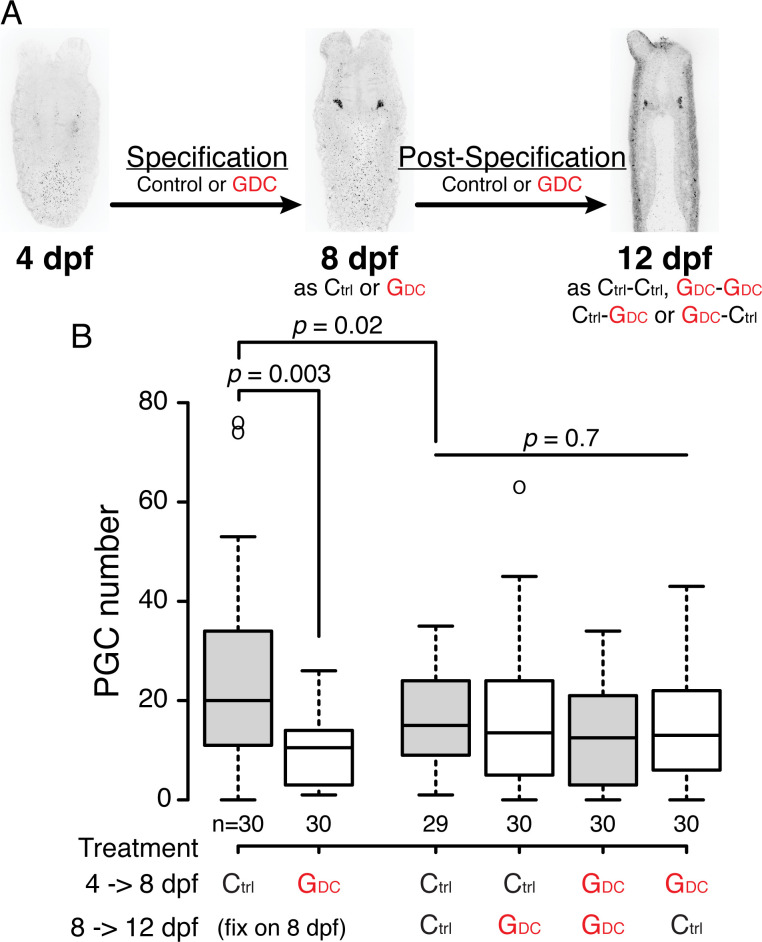
Figure 8. Inhibiting Hh signaling by GDC-0449 or Cyclopamine impairs PGC formation.
(A–D) The majority of primary polyps did not show visible developmental defects after treatment with GDC-0449 or Cyclopamine from the gastrula stage onward. (E–H) Primary polyps treated with GDC-0449 or Cyclopamine from 1 to 8 dpf formed significantly fewer PGCs than controls. p values of ANOVA tests were compared with control treatment. Scale bar = 50 µm in G. A-C are at the same scale; E–G are at the same scale.