Figure 3.
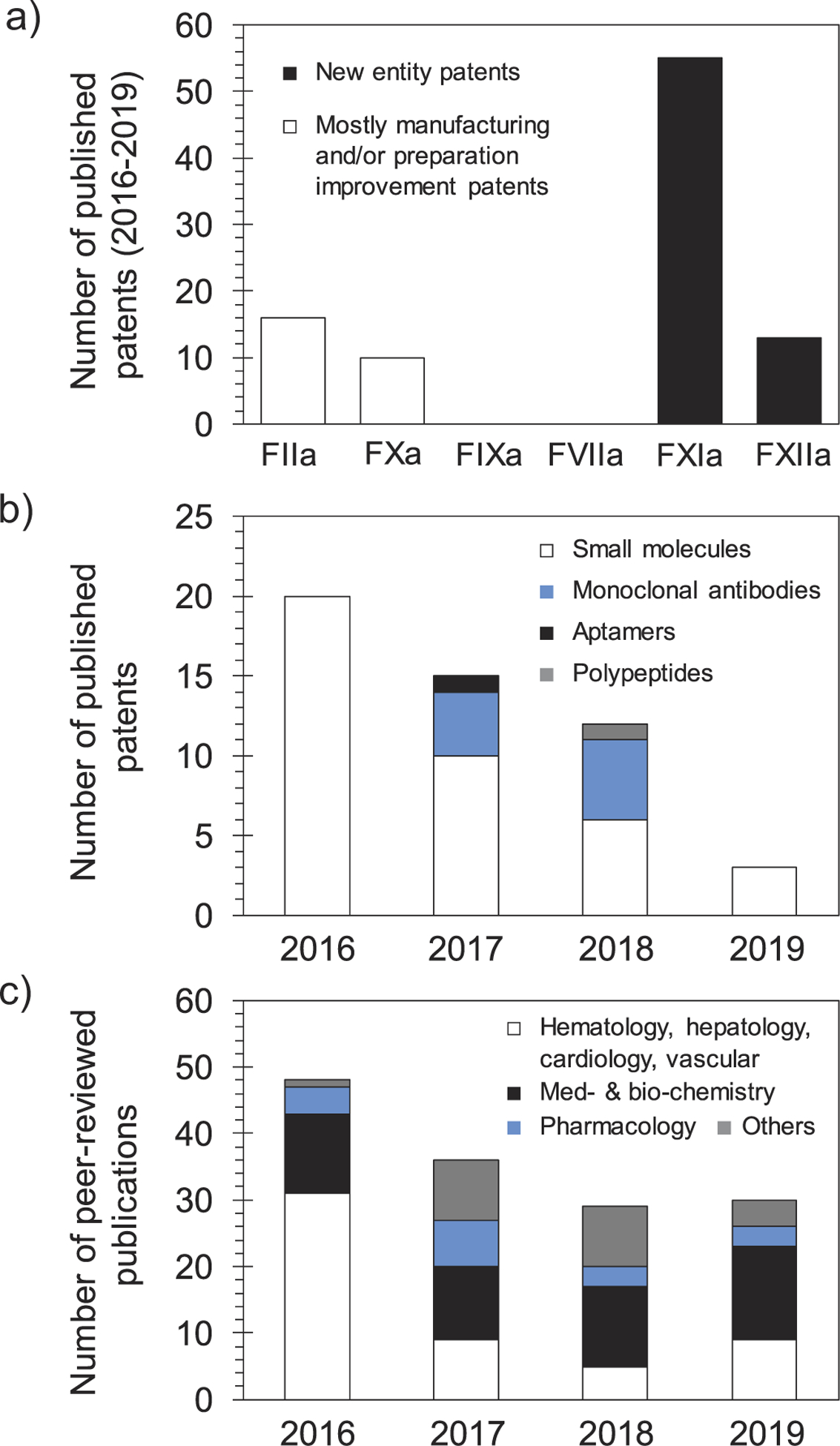
(a) A histogram shows the number of patents filed for molecules targeting different clotting factors over the 2016–2019 period. The highest number is for new molecular entities targeting FXI(a). Patents that involve FIIa and FXa inhibitors are generally to improve the manufacturing or the delivery method of approved drugs. No significant patents were retrieved for agents targeting FIXa or FVIIa. (b) A histogram shows the number of patents filed for molecular entities targeting the FXI(a) system per year starting 2016. The histogram also shows the type of molecular entities that have been claimed (small molecules, monoclonal antibodies, aptamers, and polypeptides). The claimed agents are predominantly small molecules. There is a declining trend in the number of patents filed over the 2016–2019 period, yet the number of FXI(a)-based agents that are being evaluated in clinical trials is increasing. (c) A histogram shows the number of peer-reviewed publications for topics involving FXI(a) system. The histogram highlights the most recognized areas of research. The overall declining trend in the number of FXIa publications is similar to that of patents, although publications in the areas of medicinal chemistry and biochemistry has remained steady. Data in histograms (a) and (b) were retrieved from SciFinder whereas data in histogram (c) were retrieved from Web of Science.
