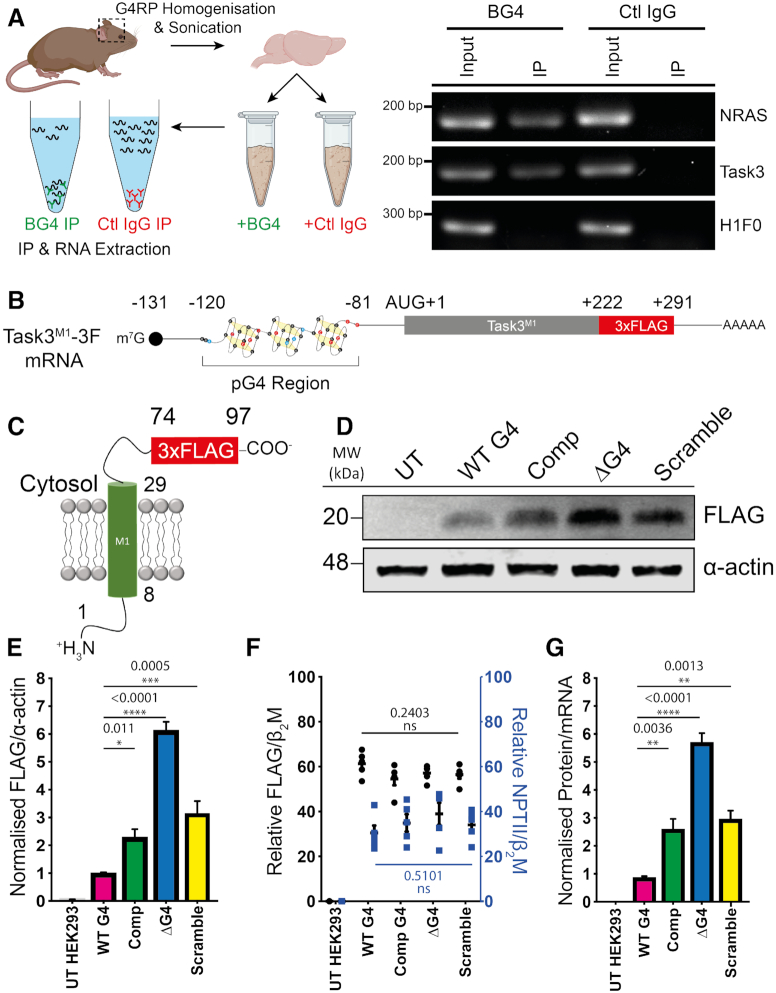
Figure 2.
The Task3 5′ UTR G4 forms in vivo and inhibits translation of Task3-FLAG peptides in vitro. (A) Outline of experimental process for in vivo BG4 RNA immunoprecipitations from mouse brain homogenates using goat BG4 and control goat IgG antibodies (left) and endpoint RT-PCRs run on 1% agarose gel for input and IP fractions of BG4 and control goat IgG immunoprecipitations (right). (B) Schematic of the mRNA transcripts produced by the different Task3 mutant 5′ UTR constructs, possessing either the wild-type full length 5′ UTR or various mutant sequences including a complementary (CCN)13 substitution, a 39 nt deletion (ΔG4) or a 39 nt scramble substitution. (C) All constructs translate the identical 97 amino acid peptides (Task3M1–3F) allowing for comparison of different translation efficiencies that arise from different structural species present within Task3 5′ UTR. (D) Western blotting of HEK-293 lysates transfected with each Task3 mutant 5′ UTR construct. (E) Quantification of Task3M1-FLAG expression normalised to α-actin expression. (F) Mutant 5′ UTR Task3M1-FLAG mRNA transcript abundance normalised to endogenous HEK-293 β2M (Black) or the internal vector control NPTII normalised to HEK-293 β2M (Blue) for transfection efficiency control. (G) Relative translation efficiency attributed to each of the wild-type or mutant Task3 5′ UTR mRNA transcripts where Task3 WT G4 5′ UTR = 1. N = 5 biological replicates where error bars represent SEM. Statistical analyses were carried out by one-way ANOVA (E – F(3, 20) = 69.9, P < 0.0001, F – FLAG: F(3, 20) = 1.56, P = 0.2403, NPTII: F(3, 20) = 0.81, P = 0.5101. G – (F(3,20) = 50.01, P < 0.0001) with post-hoc Sidak's multiple comparison tests, P-values shown. UT = untransfected.