Figure 4.
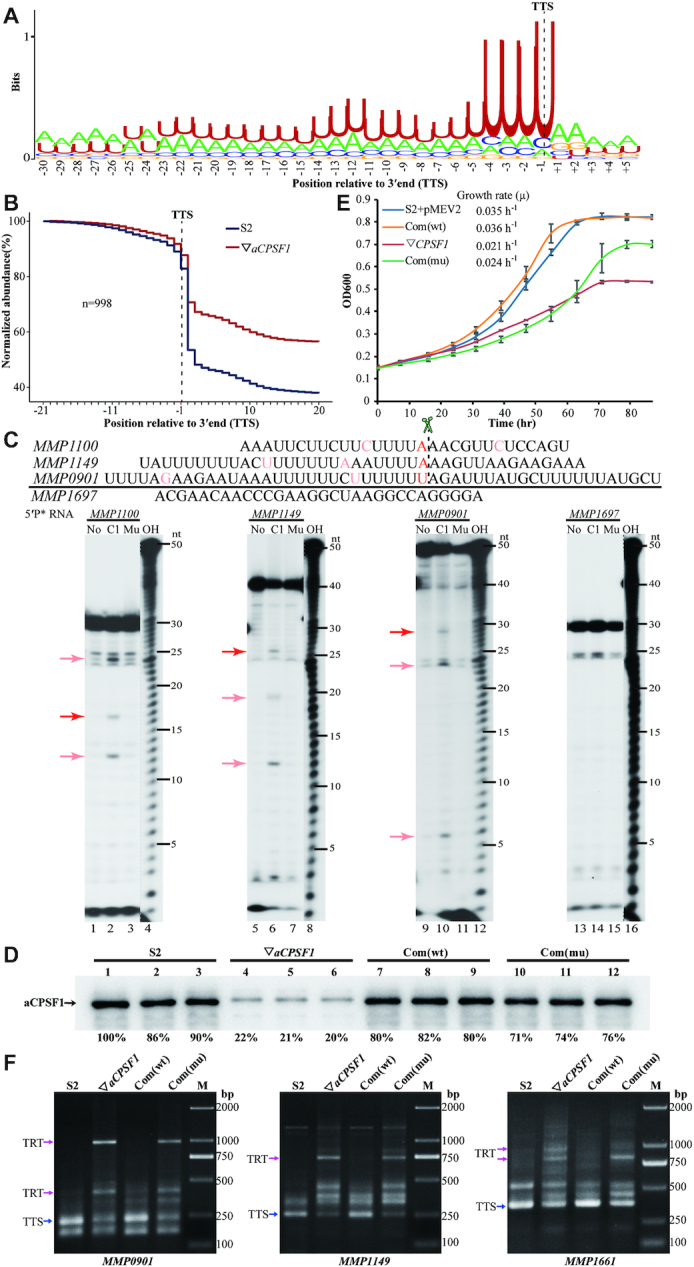
The terminator motif of M. maripaludis determined by Term-seq, and the ribonuclease activity of Mmp-aCPSF1 on the motif is essential to transcription termination. (A) Using WebLogo (v2.8.2) (41), a logo representation was generated for the sequence motif upstream of 998 primary TTSs that are defined by Term-seq. (B) A metaplot diagram shows the average reads of each 20 nt upstream and downstream of the 998 primary TTSs (dot black line) in 22°C-cultured S2 (blue line) and ▽aCPSF1 (red line). (C) The ribonuclease activity of Mmp-aCPSF1 was assayed on three representative uridine-rich RNAs derived from the TTSs (red bases) flanking sequences of MMP1100, MMP1149 and MMP0901 (upper). A uridine tract-less RNA fragment from MMP1697 was used as a control. A urea sequencing gel displays the enzymatic products (lower). No, C1, and Mu indicate the assays without, and with addition of Mmp-aCPSF1 and the catalytic inactive mutant (H243A/H246A), respectively. Red and pink arrows point to the presumed cleavage products at TTS and other sites downstream uridine-rich sequences. OH, a hydroxyl ladder indicates migrations of RNA products. (D) Western blot assays the Mmp-aCPSF1 protein abundances in three batches of 22°C-grown strains S2, ▽aCPSF1, Mmp-com(Mmp-C1) (Com(wt)) and Mmp-com(Mmp-C1mu) (Com(mu)). (E) Growth curves of the four strains were assayed on three batches of the 22°C-grown cultures, and the averages and standard deviations are shown. (F) 3′RACE assays the TRTs in 22°C-grown strains S2, ▽aCPSF1, Com(wt) and Com(mu). Blue and magenta arrows indicate the PCR products of normal terminations (TTSs) and TRTs, respectively. M, a DNA ladder indicates migrations of the PCR products.
