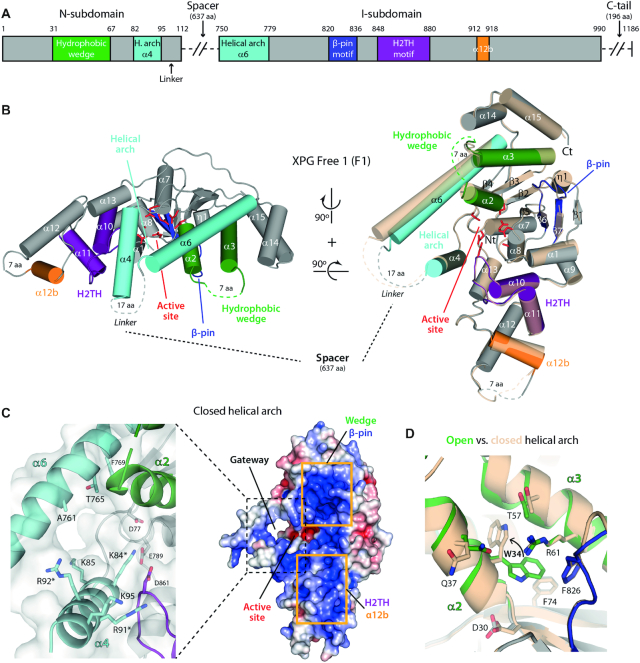
Figure 1.
Crystal structure of XPGn in the DNA-free state. (A) Bar diagram of the structural motifs in the XPG nuclease domain. The spacer and the C-terminal tail, absent in our constructs, have been omitted for simplicity. (B) Crystal structures of F1 with open and closed conformations of the helical arch. Colors are as in panel A for the closed arch conformation, while the open arch conformation is shown in transparent cream color. (C) Surface charge representation (right) and close-up view of sidechains around the gateway (left) of F1 in the closed configuration of the helical arch. Residues mutated in this work are labeled with an asterisk. (D) Comparison of residue W34 position in the open (colors as in panel A) and closed (cream color) arch conformations of F1 molecules.