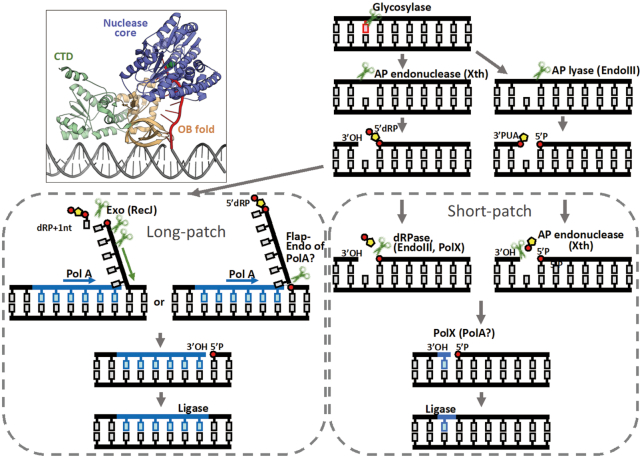
Figure 5.
Schematic of the BER pathways of D. radiodurans. Damaged bases are first removed by glycosylases. AP endonuclease Xth, or AP lyse endonuclease III, induces a nick in the bond at the 5′-side of the abasic site and creates termini with 3′-OH and 5′-dRP, or at the 3′-side of the abasic site and creates termini with 3′-PUA and 5′-P. 5′-dRP can be removed directly by dRPase, such as endonuclease III and PolX from the 3′-side of the abasic site, and 3′-PUA can be removed directly by AP endonuclease Xth from the 5′-side of the abasic site. The repair synthesis involves the insertion of one nucleotide by a gap-filling polymerase, such as PolX, or PolA, and the ligation by DNA ligase. In the long-patch BER pathway, a processive polymerase, such as PolA, mediates DNA synthesis and promotes a displacement of the downstream DNA strand. The displaced flap structure is digested by 5′-3′ exonuclease RecJ or a flap-endonuclease (such as PolA), with the resulting nick ligated by DNA ligase. A structure model of RecJ participating in long-patch BER was provided based on real crystal structures (PDB code: 5F55). Only the DNA duplex (coloured as grey) is artificially added here.