Figure 4.
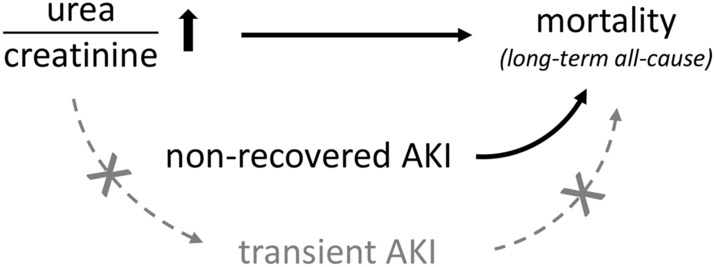
Relationship between the urea-to-creatinine ratio, different types of acute kidney injury and long-term mortality. An increased urea-to-creatinine ratio and non-recovered AKI were independent risk factors for long-term all-cause mortality. In contrast, an increased urea-to-creatinine ratio was not associated with transient AKI and transient AKI was not associated with increased long-term mortality. Black arrows denote an independent association, grey arrows denote a presumed association that was not confirmed in the current study.
