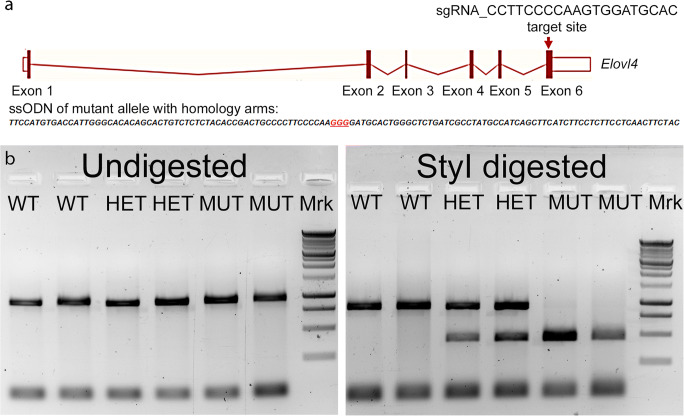
Fig. 1.
Generation and characterization of c.736T>G, p.W246G knock-in Long-Evans rat using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. a Schematic depiction of targeting strategy. The genomic region of the rat Elovl4 locus is diagrammed (the gene is oriented from left to right; total size is 28.21 kb). Solid bars represent open reading frame (exons). Open bars represent untranslated regions. The sgRNA cut site and the single-strand oligonucleotide donor sequencing with homology arms and the mutation site is shown by the red arrow. b Genotyping of WT, HET, and MUT SCA34-KI rats by StyI restriction analysis. Seven hundred four base–pair PCR products were generated from WT, HET, and MUT rats using PCR primers. The amplicons were run undigested or purified and digested with StyI restriction enzyme. Left panel: undigested amplicons ran at 704 bp for WT, HET, and MUT rats, as expected. Right panel: digestion with StyI restriction enzyme showed the WT PCR product is resistant to Sty I digestion. In contrast, HET rats show two bands, one corresponding to the WT PCR product and a smaller, digested fragment arising from the mutant PCR product containing the StyI digestion site. MUT rats show only a single band corresponding to the digested, mutant PCR product with no WT PCR product, as expected