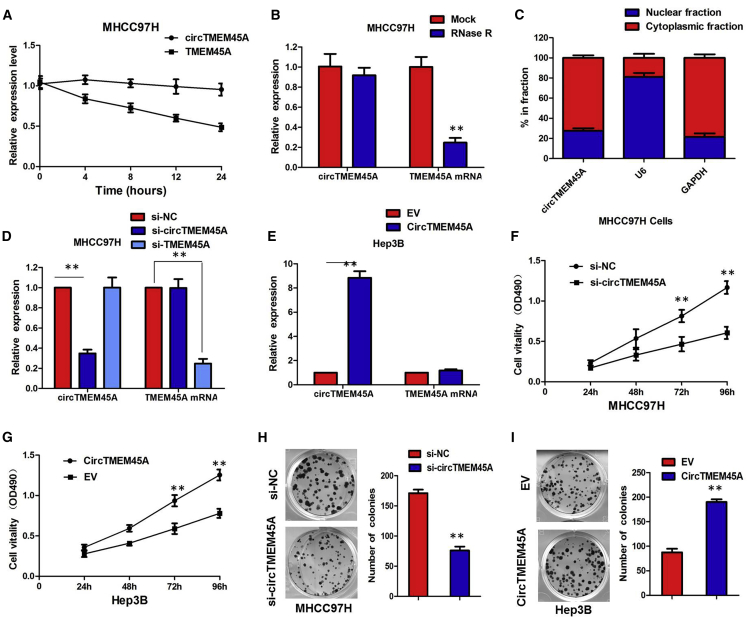
Figure 2.
circTMEM45A Loss of Function Dramatically Impairs the HCC Cell Malignant Phenotypes In Vitro
(A) Quantitative real-time PCR for the abundance of circTMEM45A and TMEM45A in MHCC97H cells treated with actinomycin D at the indicated time points. (B) Quantitative real-time PCR for the expression of circTMEM45A and TMEM45A mRNA in MHCC97H cells treated with or without RNase R. (C) Levels of circTMEM45A in the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of MHCC97H cells. (D) The expression of circTMEM45A was only downregulated by si-circTMEM45A but was not affected by si-TMEM45A. (E) The circTMEM45A expression vector markedly increased the expression of circTMEM45A compared with the empty vector. (F) CCK-8 assays showed that circTMEM45A knockdown significantly decreased the cell vitality of MHCC97H cells. (G) Overexpression of circTMEM45A promoted the proliferative ability of Hep3B cells. (H) Colony formation assays revealed that circTMEM45A knockdown greatly attenuated the numbers of visible colonies of MHCC97H cells. (I) Colony formation assays revealed that overexpression of circTMEM45A greatly increased the numbers of visible colonies of Hep3B cells. All tests were performed at least three times. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.