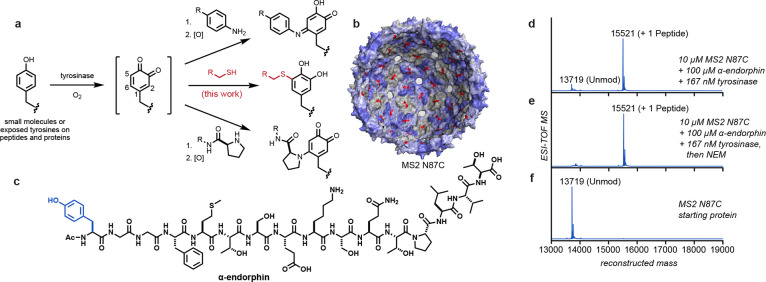
Figure 1.
Tyrosinase-mediated oxidative coupling reactions. (a) Phenols are oxidized by tyrosinase to yield o-quinone intermediates that couple with a variety of nucleophiles on biomolecules. This work explored the addition of cysteine thiolates (shown in red). (b) Structure of the MS2 viral capsid (PDB ID 2MS2), with 180 interior cysteine residues (N87C) indicated in red. Pores in the capsid shell allow the entry of peptides and small molecules. (c) Structure of α-endorphin, with the targeted tyrosine residue shown in blue. (d–f) Coupling reactions were screened using ESI-TOF MS, showing full modification of the MS2 N87C capsid without off-target oxidation. Reaction conditions: pH 6.5 phosphate buffer, RT, 30 min. Expected mass values: MS2 N87C [M + H]+ = 13719; MS2 N87C–N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) adduct [M + H]+ = 13844; MS2 N87C–endorphin o-hydroquinone product [M + H]+ = 15521.