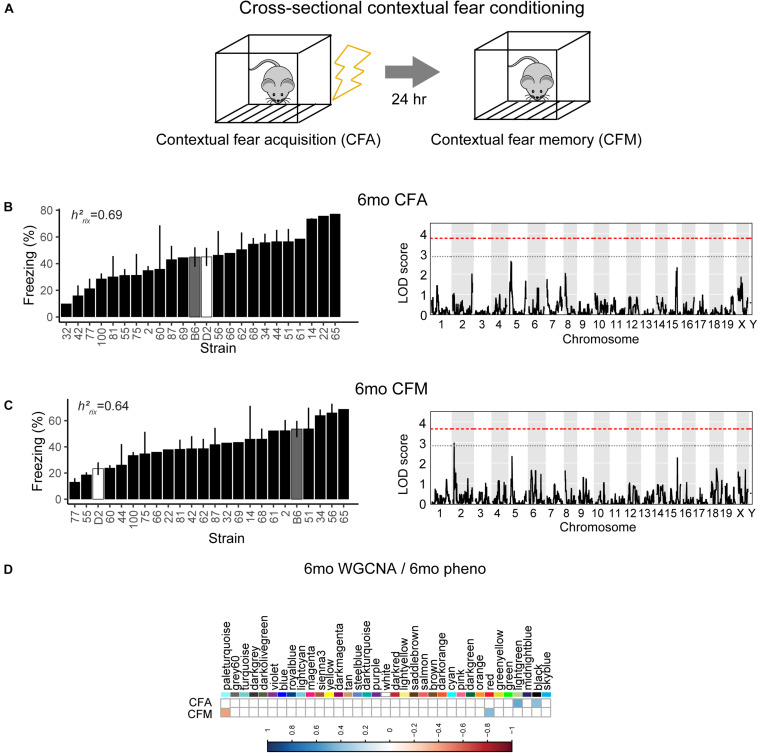
FIGURE 3.
Variation in short- and long-term memory is heritable and not controlled by a single genetic mechanism at 6 months of age. (A) B6-BXD mice underwent contextual fear conditioning to assess short- and long-term memory. Mice received four mild footshocks and were tested for contextual memory by measuring freezing 24 h later. (B) Contextual fear acquisition, or freezing during the postshock 4 (PS4) interval, was heritable (h2RIx̄ = 0.69) at 6 months. QTL mapping revealed that no locus was significantly associated with performance on contextual fear acquisition. (C) Contextual fear memory performance is also highly heritable (h2RIx̄ = 0.64); however, QTL mapping failed to identify significant loci controlling contextual fear memory. (D) Four WGCNA modules were associated with contextual fear conditioning traits at 6 months: CFA was significantly associated with the lightgreen and black modules’ expression. CFM was significantly associated with the paleturquoise and red modules’ expression. QTL significance thresholds: red line, alpha = 0.05; black line, alpha = 0.33.