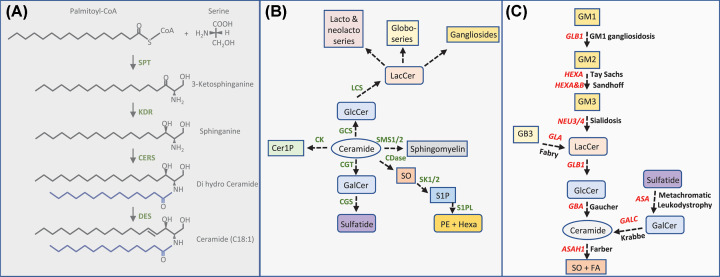
Figure 1. Metabolism of glycosphingolipids.
(A) Schematic representation of the de novo synthesis of sphingolipids. SPT: serine palmitoyltransferase. KDR: ketoreductase. CERS: ceramide synthase. DES: desaturase. The acylchain is depicted in blue and can range from C14-C26 depending on the CERS enzyme involved in acyl chain condensation (six CERS members exist). Depending on the acyl-CoA moiety used by SPT, i.e. myristoyl-CoA, palmitoyl-CoA or stearyl-CoA different sphingoid bases can be produced (C16:1, C18:1 or C20:1). (B) Generation of ceramide derived species including glycosphingolipids. CK: ceramide kinase. GCS: glucosylceramide synthase. SMS: sphingomyelin synthase. CGT: UDP-galactose ceramide galactosyl transferase. CGS: cerebroside sulfotransferase. CDase: ceramidase. SK: sphingosine kinase. S1PL: S1P lyase. LCS: lactosylceramide synthase. Cer1P: ceramide-1-phosphate. GlcCer: glucosylceramide. LacCer: lactosylceramide. GalCer: galactosylceramide. SO: sphingosine. S1P: sphingosine-1-phosphate. PE: phosphatidylethanolamine. Hexa: hexadecanal. (C) Lysosomal degradation of GSL with responsible gene products and diseases connected to defects. GLB1 (β-galactosidase), HEXA (β-hexosaminidase A), HEXB (β-hexosaminidase B), NEU3/4 (neuraminidase 3/4), GLA (α-galactosidase A), GBA (β-glucocerebrosidase), ASA (Arylsulfatase A), GALC (β-galactosylceramidase), ASAH1 (acid ceramidase).