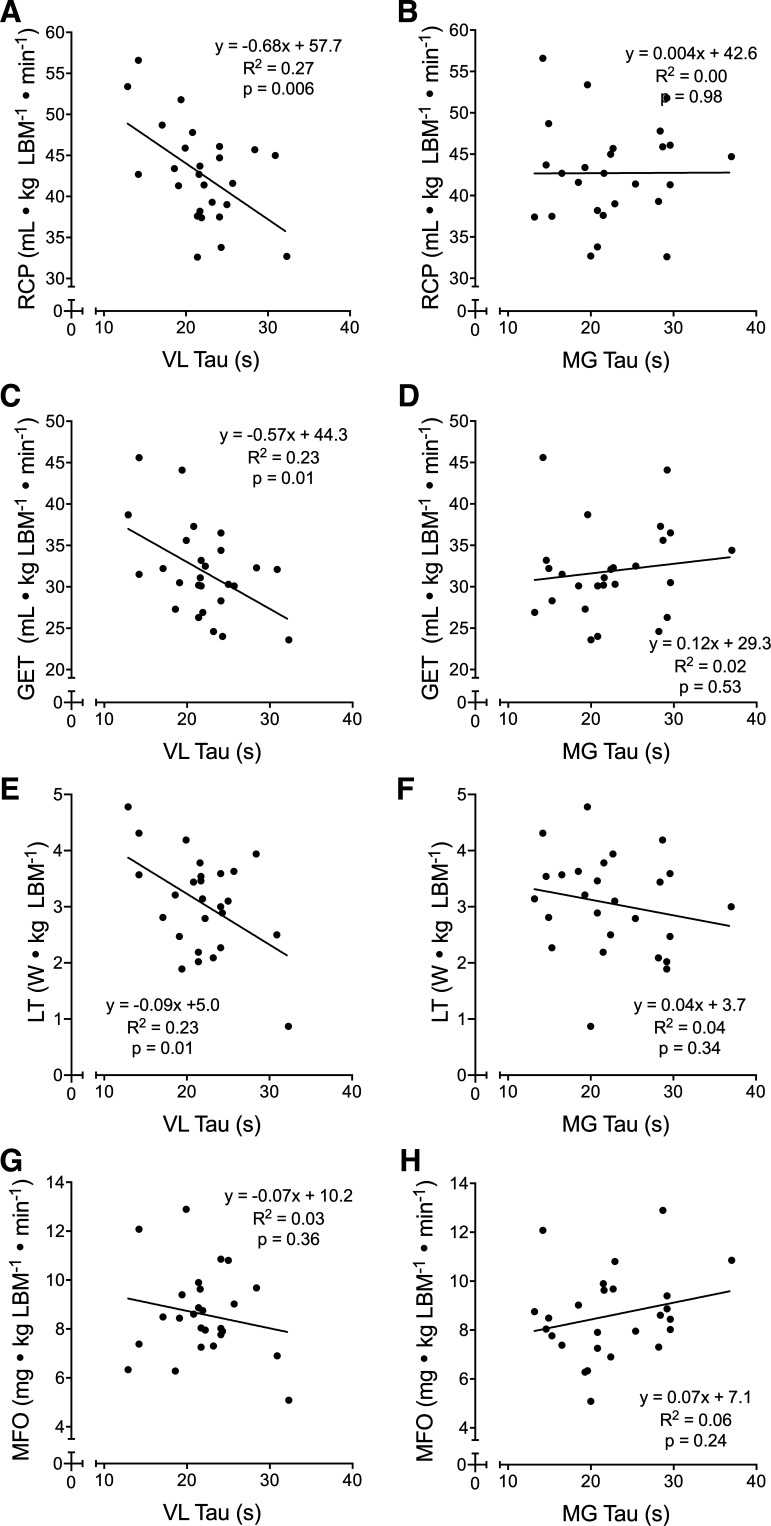
Fig. 5.
Scatterplots of various indices of submaximal aerobic fitness and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS)-derived skeletal muscle oxidative capacity in the vastus lateralis (VL) and medial gastrocnemius (MG). The VL oxidative capacity was significantly correlated with the respiratory compensation point (RCP), gas exchange threshold (GET), and lactate threshold (LT) (A, C, and E) but not maximal rates of fat oxidation (MFO; G). The MG oxidative capacity was not correlated with any of these variables (B, D, F, and H). For all plots, n = 26 (13 females, 13 males). Linear regression equations, coefficients of determination (R2), and P values are displayed for each plot.