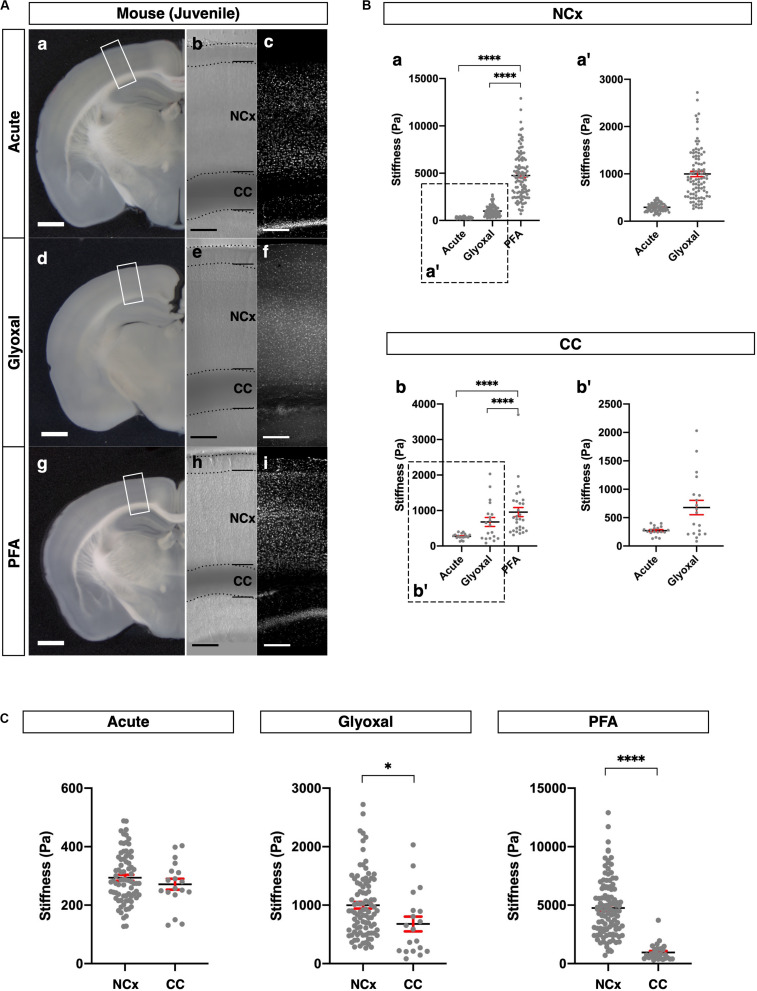
FIGURE 3.
Comparison of tissue stiffness in juvenile mouse brains in different fixatives. (A) (a, d, and g) Representative images of 4-week-old mouse brain slices: (a) acute, (d) glyoxal-fixed, and (g) PFA-fixed. (b, e, and h) Phase-contrast images of brain slices set on AFM: (b) acute, (e) glyoxal-fixed, and (h) PFA-fixed. Note that CC shows dark color because of an optical filter setting. (c, f, and i) DAPI images: (c) acute, (f) glyoxal-fixed, and (i) PFA-fixed. (B) Comparison of stiffness in NCx (a) and CC (b) in different fixatives. (a′ and b′) Magnified views of insets in (a and b), respectively. (C) Comparison of stiffness between NCx and CC in each fixative. NCx, neocortex; CC, corpus callosum; scale bar: 1 mm for (A) (a, d, and g); 200 μm for (A) (b, c, e, f, h, and i). One-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test; P < 0.0001 (****) for (B). Two-tailed unpaired t-test; P < 0.05 (*) and P < 0.0001 (****) for (C). Error bars in graphs are represented as the mean ± SEM.