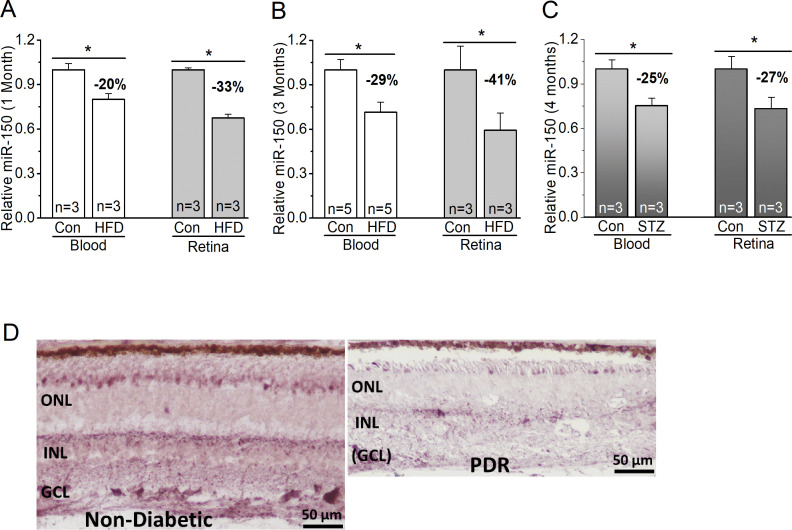
Figure 1.
MiR-150 is decreased in diabetic eyes. (A–C) The blood serum (blood) and retina were collected from mice to detect the levels of miR-150. (A, B) MiR-150 is decreased in the serum and retina of mice fed with a HFD compared with the control mice fed with a normal chow (Con) for 1 month (A) or 3 months (B). (C) Using the STZ-induced T1D mouse model, 4 months after the STZ-injections, the STZ-T1D mice (STZ) also have decreased miR-150 in the serum and retina compared with the control mice injected with a citric buffer (Con). Student’s t-test, *p<0.05. (D) The in situ hybridization of miR-150 in retinal sections from a non-diabetic age-matched donor (left) and from a patient with PDR (right) shows a qualitative decrease of miR-150 in the retina of PDR. Con, control; GCL, ganglion cell layer; HFD, high-fat diet; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; PDR, proliferative diabetic retinopathy; STZ, streptozotocin; T1D, type 1 diabetes.