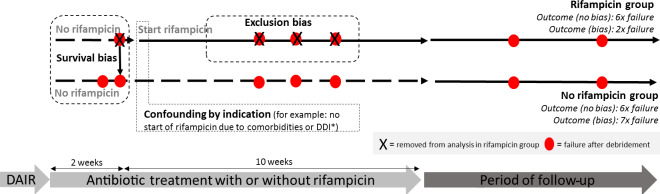
Figure 1.
Hypothetical example of a prosthetic joint infection (PJI) study with a flawed outcome induced by methodological errors. Example of a PJI cohort, retrospectively stratified by use of rifampin. Survival bias occurs because only patients that “survive” the first weeks until the start with rifampin are analyzed in the rifampin group. All failures before start of rifampin will be analyzed in the non-rifampin group. Confounding by indication occurs when patients with certain risk factors for failure (e.g., comorbidities, drug–drug interactions, severely ill) are not selected for treatment with rifampin. Exclusion bias occurs if patients are excluded while they are still using rifampin, as only failures within the rifampin group can be excluded. In this hypothetical example assuming comparable treatment strategies, both groups would have an identical failure rate without bias (both six failures) but 3 times as much failure in the non-rifampin group after introduction of bias. DDI: drug–drug interaction; f/u: follow-up. DAIR: debridement, antibiotics, implant retention.