FIGURE 1.
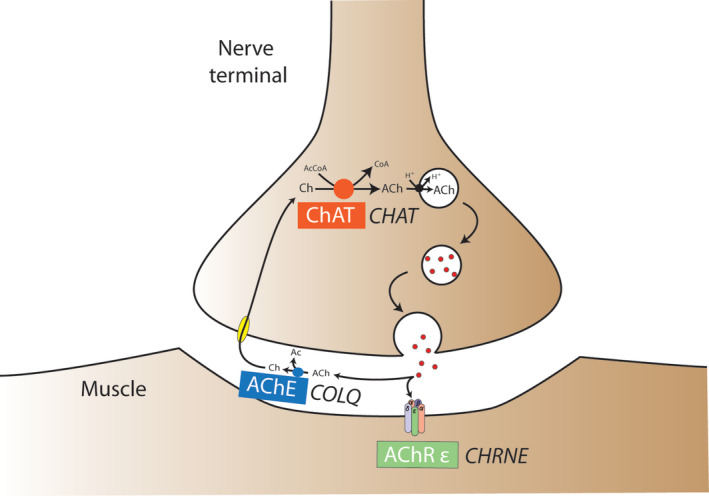
Schematic illustration of currently reported CMSs in dogs and cats including the affected neuromuscular compartment, the mechanism of failure of neuromuscular transmission, the affected protein, and the underlying mutated gene. Ac, acetyl; AcCoa, acetyl‐coenzyme A; ACh, acetylcholine; AChE, acetylcholinesterase; AChR ε, acetylcholine receptor ε subunit; Ch, choline; ChAT, choline acetyltransferase protein; CHAT, choline acetyltransferase gene; CHRNE, cholinergic receptor nicotinic ε subunit gene; CoA, coenzyme A; COLQ, collagen‐like tail subunit of asymmetric acetylcholinesterase gene; CMS, congenital myasthenic syndrome; H+, hydrogen ion
