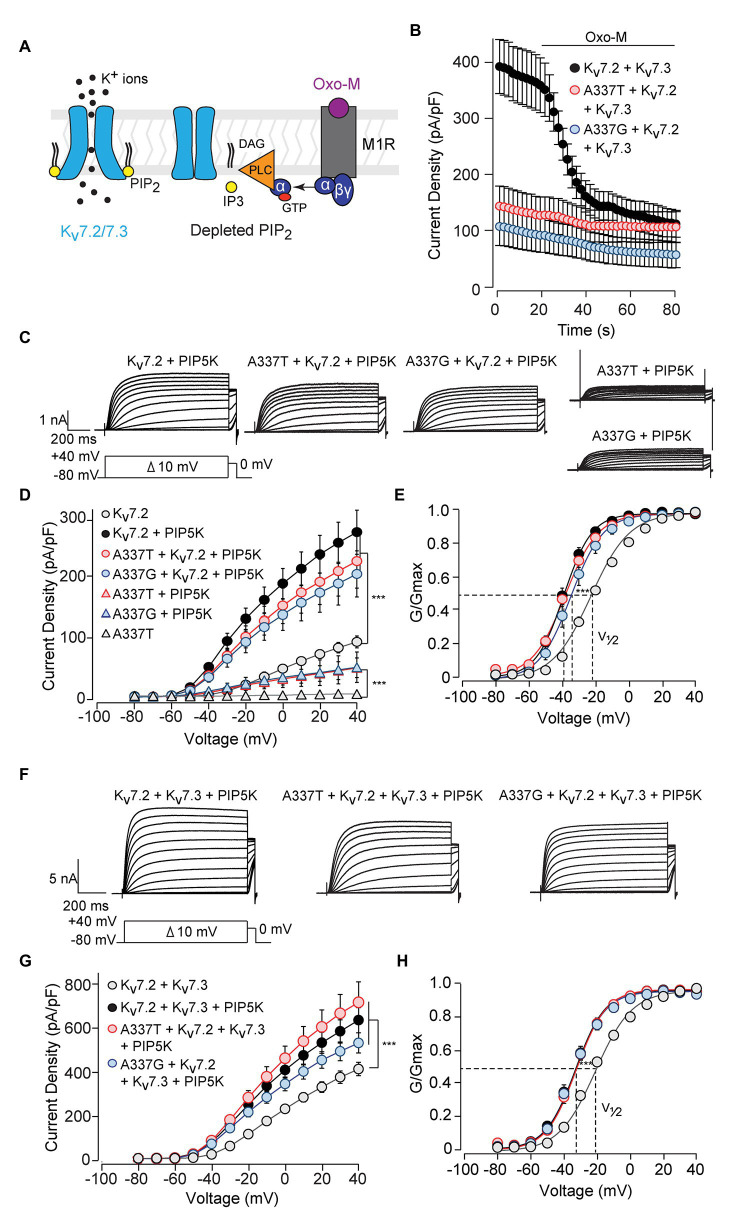
Figure 5.
Currents suppressed by A337 variants were restored by co-expression of PIP5K. (A) Diagram of the main transduction pathway underlying cholinergic inhibition of M-current. Agonist oxotremorine methiodide (Oxo-M) activates the M1 muscarinic receptor (M1R), activating a heterotrimeric G-protein (α, βγ) and phospholipase C (PLC). PLC cleaves phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) residing in the membrane, reducing PIP2 available for binding to the channel. (B) Time course of current inhibition by Oxo-M (10 μM, bar) in CHO cells transfected with M1R, Kv7.2, and Kv7.3, with and without A337 variants. (C) Representative families of currents produced in response to step depolarizations by the indicated combinations of WT and mutant Kv7.2 subunits when co-transfected with PIP5K. (D) Current-voltage relationships for channels co-expressed with PIP5K compared to without PIP5K (***p < 0.001, two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni test, n = 5–16, see Table 1). (E) Conductance-voltage relationships from cells transfected with PIP5K compared to WT Kv7.2 without PIP5K. Activation of WT Kv7.2 expressed alone, WT + A337T, and WT + A337G are significantly shifted to hyperpolarized potentials (***p < 0.001, two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni test, n = 5–16, see Table 1). (F) Representative currents produced by the indicated combinations of heteromeric WT and mutant Kv7.2 subunits in cells co-transfected with PIP5K. (G) Current densities in cells co-expressing PIP5K compared to WT Kv7.2 + Kv7.3 (***p < 0.001, Two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni test, n = 10–20). (H) Conductance-voltage relationships from cells transfected with PIP5K compared to WT Kv7.2 + Kv7.3 expressed without PIP5K. PIP5K overexpression shifts activation significantly to hyperpolarized potentials (***p < 0.001, two-way ANOVA, Bonferroni test, n = 10–20, see Table 1).