Fig. 5: The PRG-1/Piwi pathway is required for transgenerational inheritance of pathogenic aversive learning.
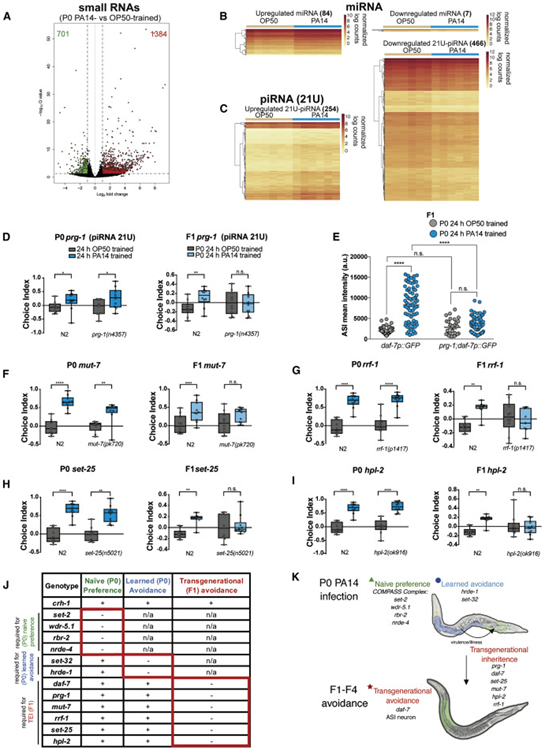
(A) PA14-upregulated (1364, red) and downregulated (701, green) small RNAs were differentially expressed using DESeq2. Volcano plot shown at FDR < 5% and log2 fold change > and < 1. Regularized expression counts from differentially expressed miRNAs (B) and piRNAs (C) in P0 animals. (D) prg-1(n4357) mutants are defective for transgenerational inheritance of pathogenic avoidance. (E) Elevated daf-7p::gfp expression is abrogated in progeny of prg-1 PA14-trained mutants. (F-I) mut-7(pk720), rrf-1(pk1426), set-25(n5021), and hpl-2(ok916) P0s have normal naïve preference and can learn to avoid PA14 after training; however, naïve progeny are defective for inherited avoidance. One-Way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparison test, mean ± SEM. n ≥ 7 choice assay plates with 50-200 worms. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns = not significant. (J, K) Naïve C. elegans prefer PA14, which requires the activity of the COMPASS complex (SET-2, WDR-5.1, and RBR-2) and NRDE-4. After infection by PA14, C. elegans learn to avoid PA14, which requires HRDE-1 and SET-32. piRNA pathway components (PRG-1, MUT-7, RRF-3, RRF-1), and histone modification regulators (SET-25 and HPL-2) are required to transmit transgenerational inheritance of pathogenic avoidance from the P0-F1. daf-7 expression is induced in the ASI neuron, and daf-7 and ASI are required for avoidance in the F1 generation. daf-7 levels in the ASI may set the avoidance response ability of that generation, rendering the animals “primed” for increased expression of daf-7 in the ASJ and subsequent avoidance upon PA14 encounter. (Yellow = neurons, Blue = intestine, Green = germline.). Table: genes are characterized by their requirement for normal naïve preference for PA14 (green), Learned avoidance (blue), and Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance (red).
