Figure 7.
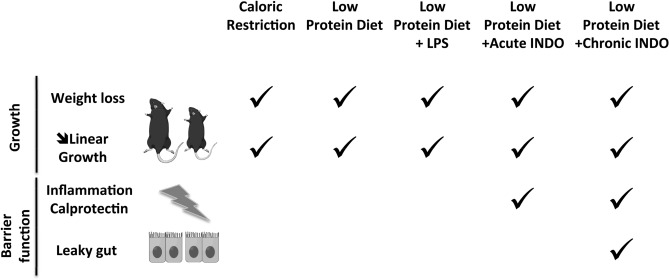
Undernutrition leads to growth failure and is often associated to environmental enteric dysfunction (EED). We aimed to develop a preclinical model of undernourished model with environmental enteropathy features such high intestinal inflammation and intestinal permeability. To induce undernutrition with EED, post-weaning C57BL/6 mice were fed with malnourished diet alone or combined with a gastrointestinal insult trigger. Growth was assessed by body weight and tail length. Intestinal permeability and inflammation were used as enteropathic markers. CR and LP for 3 weeks induced stunting and wasting but had no intestinal impact. We therefore decided to combine LP diet to a gastrointestinal insult trigger by liposaccharides (LPS) or indomethacin. LPS did not significantly impact small intestine while indomethacin increased fecal calprotectin production. To accentuate the effects, we investigated the effects of repeated gavages of indomethacin in addition to LP diet and mice exhibited stunting and wasting with intestinal hyperpermeability and gut inflammation.