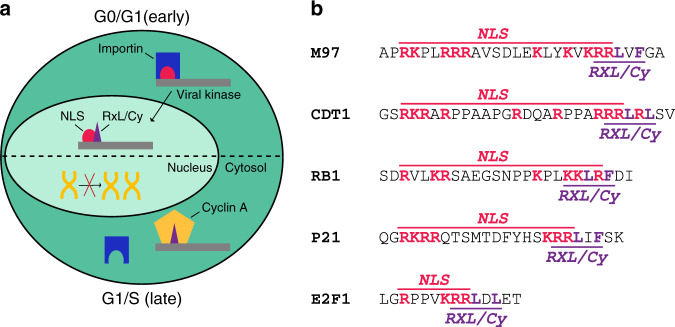
Fig. 6. The NLS-RXL module is conserved across several cell cycle regulators.
a A model summarizing the function of the NLS-RXL/Cy module in infected cells. In the absence of Cyclin A (G0/G1, early), the NLS of M97 is functional and M97 is imported into the nucleus. MCMV induces Cyclin A and drives the cell cycle towards an S-phase environment (G1/S, late). Cyclin A binds to the RXL/Cy motif on M97 and masks the NLS, leading to cytosolic accumulation of M97–Cyclin A complexes. Cellular DNA synthesis is inhibited due to mislocalized Cyclin A. b Conservation of RXL/Cy-NLS modules across several cellular cell cycle regulatory proteins. The depicted sequences are of human origin.