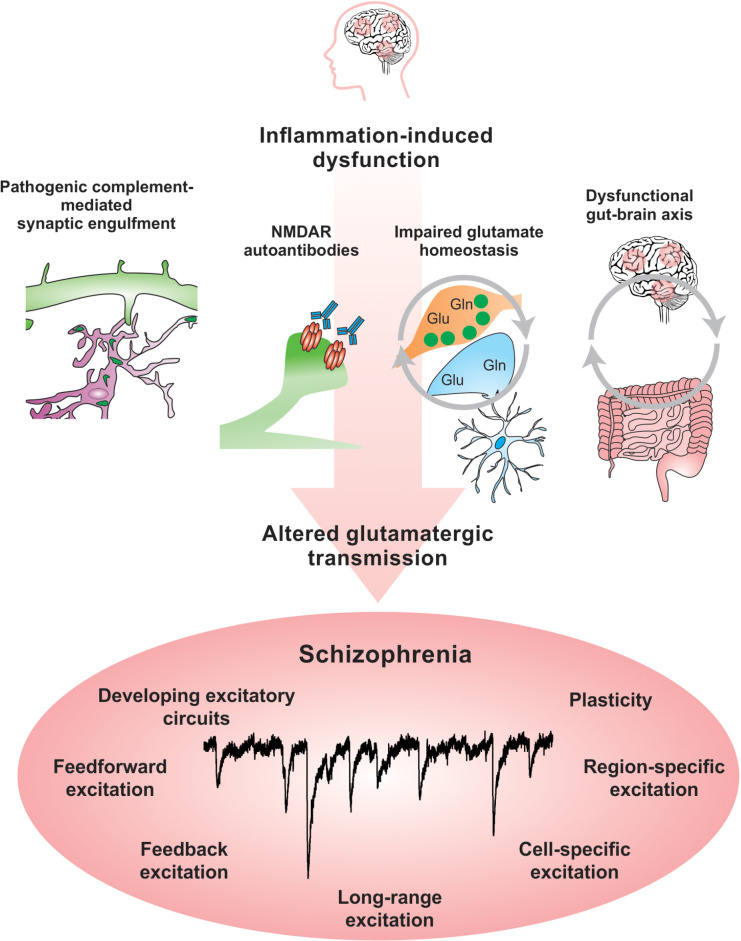
FIGURE 4.
Neuroinflammation-induced dysfunctions that alter glutamatergic transmission in SCZ. Changes in glutamatergic transmission are known to occur in SCZ. Neuroinflammation impacts excitatory circuitry in SCZ through complement-mediated engulfment of excitatory synapses, the production of autoantibodies against NMDARs, changes in glutamate homeostasis potentially mediated by alterations in astrocytes and changes in the gut-brain axis, a known regulator of glutamate synthesis that is able to impact CNS functions such as stress responses. These changes in excitatory transmission can alter brain circuitry, for example, by altering synaptic plasticity and long-range excitation.