Figure 1.
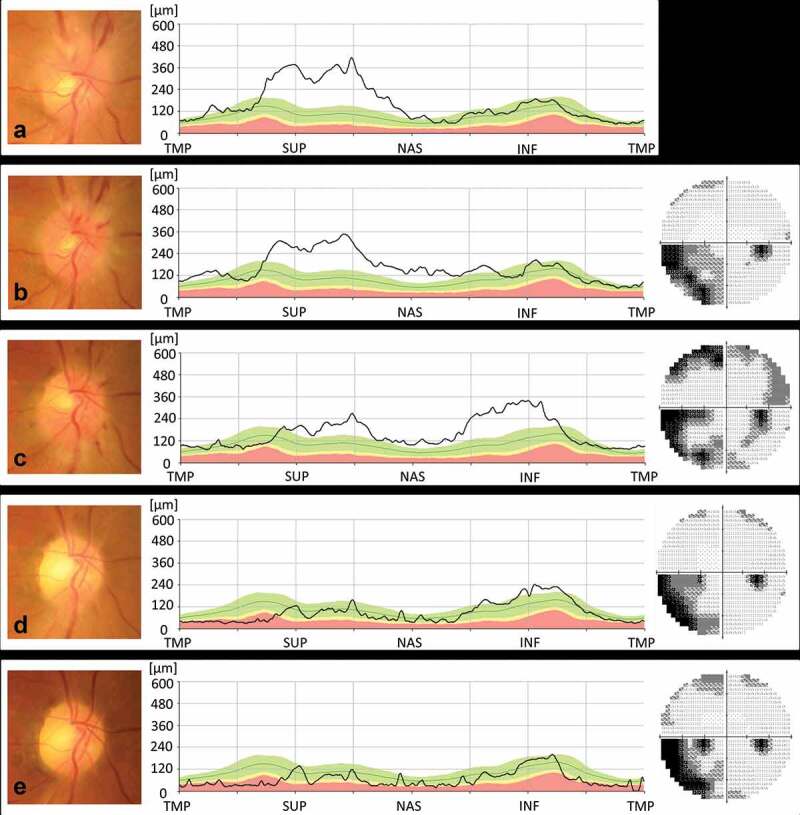
(a). At initial examination, swelling was noted in the superior portion of the right optic disc. BCVA was 30/20 in the right eye. (b). Over the next seven days, optic disc swelling, and nasal and peripapillary haemorrhage developed, but his BCVA did not change. Visual field testing showed an inferonasal visual field defect. (c). One month later, the BCVA decreased to 20/50, and the inferior portion of the right optic disc was swollen. Visual field testing detected a new upper visual field defect. (d). Following treatment with 40 mg of prednisone daily for a week followed by a reduction in dosage of 10 mg every week, optic disc swelling was no longer present. BCVA increased to 30/50, and the visual field improved. (e). The patient’s visual function remained unchanged for the next six months; however, RNFL thinning subsequently developed in the infero-temporal part of the right optic disc.
NAION = non-arteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy; BCVA = best corrected visual acuity; TMP = temporal; SUP = superior; NAS = nasal; INF = inferior.
