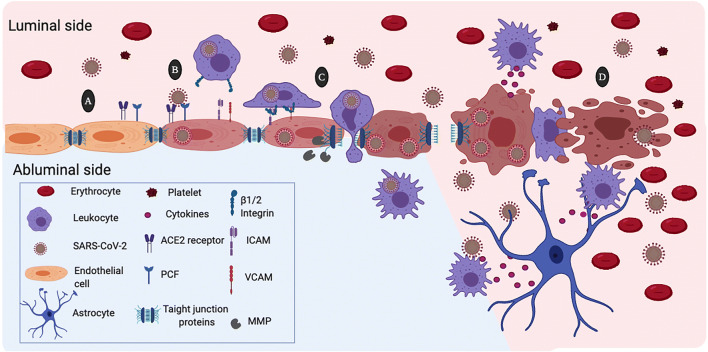
Fig. 2.
Possible mechanism of damage to the blood-brain barrier (BBB) by the action of SARS-CoV-2. a Expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the pro-protein convertase furin (PCF) in the membrane of the brain microvascular endothelial cells facilitates SARS-CoV-2 infection. b SARS-CoV2 infection activates the brain microendothelial cells inducing high expression of the vascular and the intercellular adhesion molecules (VCAM and ICAM). Likewise, SARS-CoV-2 induces the expression and activation matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) that degrade tight junctions proteins. c Recognition of ICAM and ICAM through the β1 and β2 integrins causes binding of circulating leukocytes to endothelial cells that lead transcellular extravasation. This process facilitate viral entrance to the cerebral parenchyma through the “Trojan horse” mechanism. d SARS-CoV-2 viral replication induces endothelial cell contraction and lysis. Increased permeability of the BBB allows extravasation of plasma proteins and blood cells. Activation of leukocytes and platelets contributes to the BBB damage. Besides, endothelial cell death disturbs the microenvironment of the brain parenchyma allowing free passage of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and infection of other cells of the central nervous system