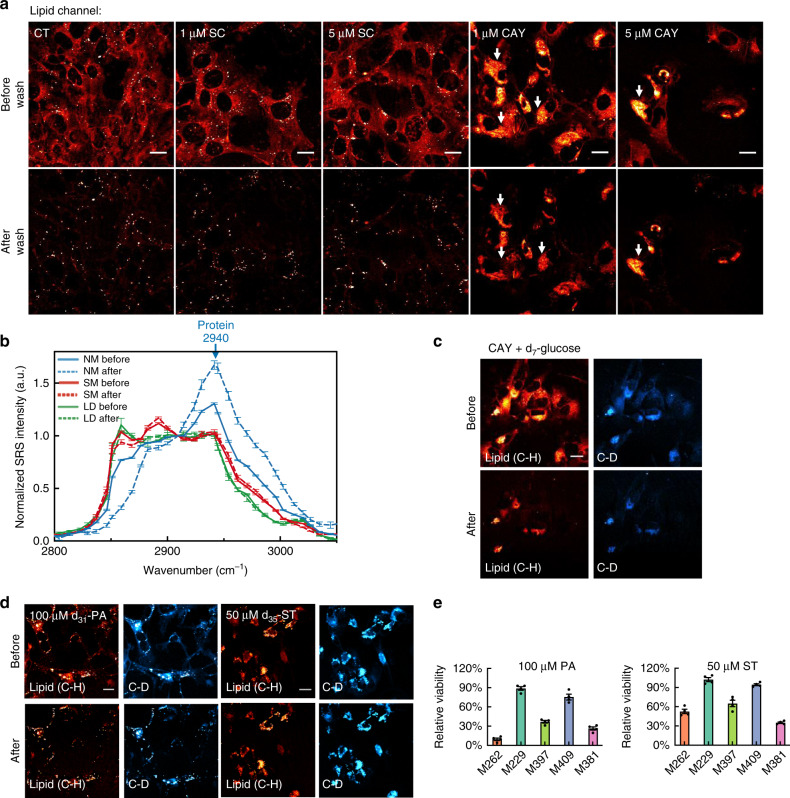
Fig. 5. Formation of intracellular phase-separated solid membrane (SM) domains induced by mono-unsaturation inhibition.
a Representative lipid-channel SRS images from the same set of M381 cells before (top) and after (bottom) detergent wash in control (CT), with SC or CAY treatment. Detergent-resistant SM structures are arrow indicated. b Normalized (to 2908 cm−1) hSRS spectra on the same NM (normal membrane, blue), SM (red), and LDs (green) structures in M381 cells from before (solid-lined) and after (dash-lined) detergent wash. (n = 7, 12, 6 for NM, SM, LD, respectively, blue arrow indicates the protein peak at 2940 cm−1). c SRS images at the lipid (C-H) and the C-D channels on the same set of M381 cells growing in d7-glucose medium with 1-day 5 μM CAY before (top) and after (bottom) detergent wash. d SRS images at the lipid (C-H) and the C-D channels on the same set of M381 cells with 3-day d31-palmitic acid (d31-PA) or d35-stearic acid (d35-ST) treatment before (top) and after (bottom) detergent wash. e Relative cellular viability with 3-day PA or ST treatment (n = 4 independent experiments). Scale bars, 20 μm. Data shown as mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source data file.