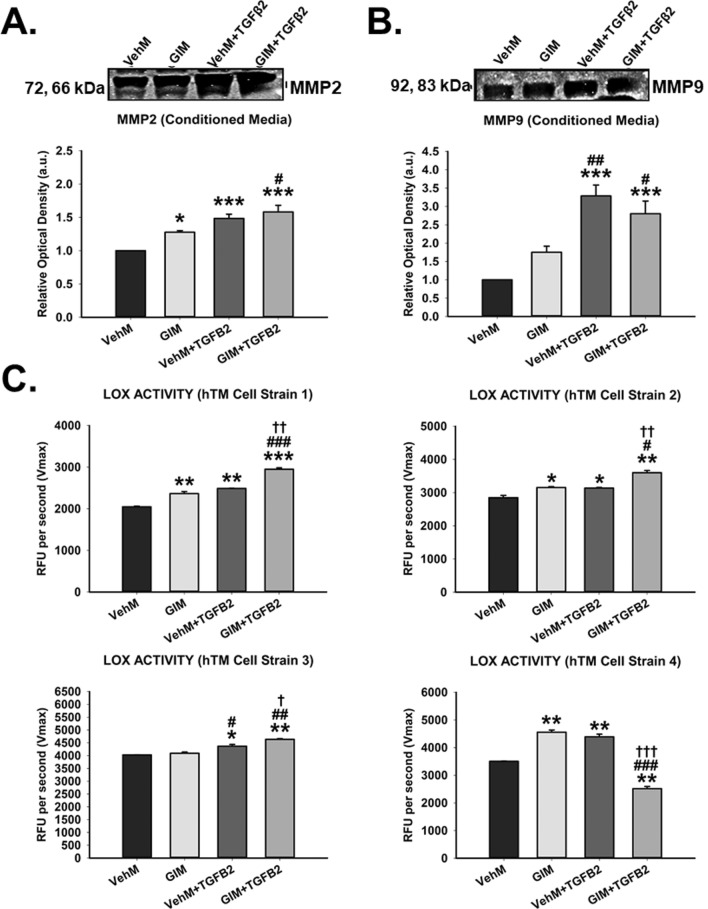
Figure 8.
GIMs increase activities of MMP2 and MMP9 together with LOX in the presence or absence of TGFβ2 in conditioned media. Conditioned medium from primary hTM cells cultured on vehicle control (VehMs) or GIM substrates for 7 days were collected and normalized to total protein concentration prior to determining enzyme activity in each sample. Gelatin Zymography was used to determine enzyme activity of specific MMPs in the absence or presence of TGFβ2. Representative cropped gel bands of (A) MMP2 and (B) MMP9 enzymatic activity. Full length gel zymograms are shown in Supplementary Fig. S9. (C) Lysyl oxidase enzyme activity was determined as the Vmax (in RFU units per second) for four different cell strains. Columns and error bars; means and standard error of mean (SEM). One-way ANOVA with the Tukey pairwise comparisons post hoc test was used for statistical analysis. (n = 4 biological replicates. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for the group of interest versus control, VehM. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 for the group of interest versus GIM. †p < 0.05, ††p < 0.01, †††p < 0.001 for VehM + TGFβ2 versus GIM + TGFβ2). hTM, human trabecular meshwork. Densitometric analyses of the zymographs was done using ImageJ 1.8.0_112 software (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/, 1997–2018). Enzyme activity was measured using the SoftMax Pro 7 Data Acquisition and Analysis Software (Molecular Devices; https://www.moleculardevices.com/products/microplate-readers/acquisition-and-analysis-software/softmax-pro-software).