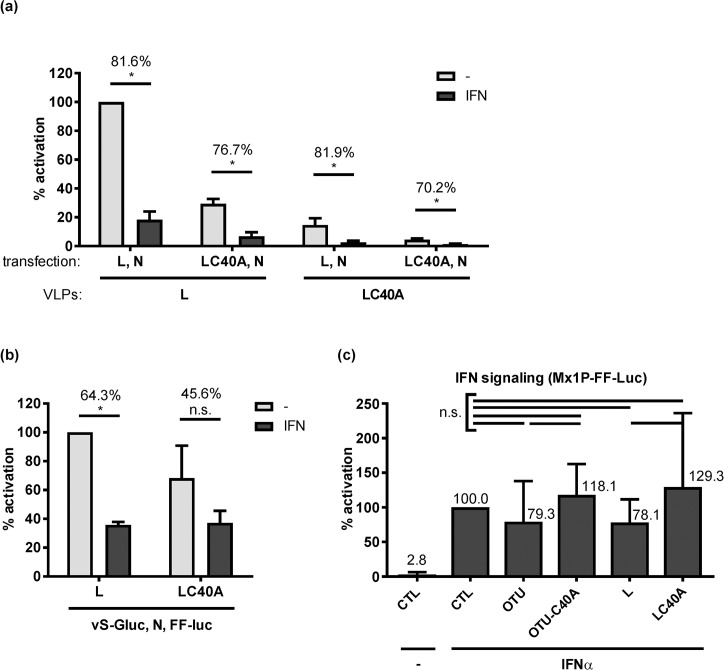
Fig 4. IFN effect on wt and C40A L.
(a) tc-VLP activity in indicator cells. Cells were transfected with L and N support plasmids and incubated 24 h later with either medium (-) or medium containing 1,000 U/ml of IFN-α B/D (IFN). Combinations of wt and C40A mutant L were used to produce and support VLP activity in donor and indicator cells, as indicated. Infection with the L-tc-VLPs or the LC40A-tc-VLPs was performed 20 h post-interferon. (b) RdRP activity of wt and C40A L in the minireplicon system. BSR-T7/5 cells were mock treated or treated with 1000 IU/ml IFN at 24 h after transfection. Luciferase activities were measured 24 h post-infection (a) or 44 h post-interferon (b). Reporter values were normalized to the inactive L polymerase (LΔDD) condition that was transfected in parallel, and expressed as percentage of the wt L under untreated (-) condition. The percentage of reduction of luciferase activity between untreated and IFN-treated conditions is written on top of the histogram bars. (c) Influence of overexpressed OTU or full-length L on IFN signaling. HuH-7 cells were pretransfected with expression constructs and the reporter plasmid pGL3-Mx1P containing the FF-Luc gene under control of the IFN-responsive mouse Mx1 promoter [38]. IFN signalling was triggered by treating cells with 1,000 U/ml IFN at 4 h post-transfection and luciferase activities measured at 20 h post-transfection. Mean values and standard deviations of 3 (a, b) or 5 (c) independent experiments are shown. Statistical testing was performed as indicated for the previous figures. *, P < 0.05; n.s., not significant.