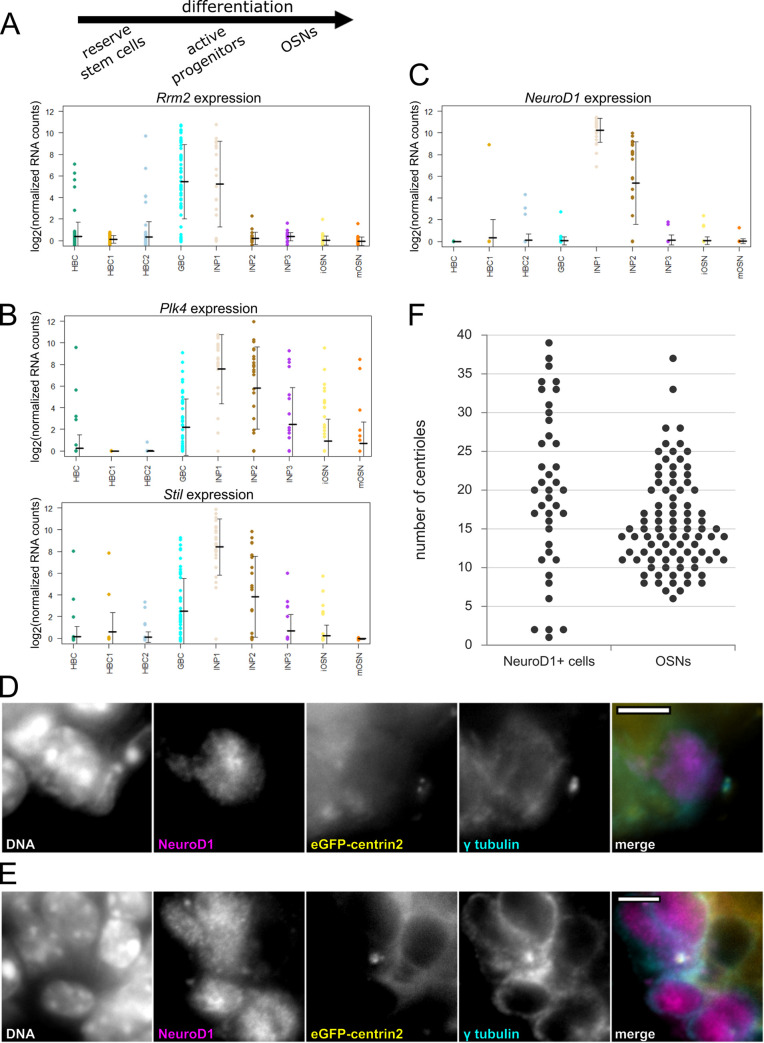
Fig 3. Plk4 and Stil RNA levels and centriole number in early immediate neuronal precursors in the olfactory epithelium.
(A-C) Secondary analysis of an existing single-cell RNA sequencing data set from Fletcher and colleagues compares RNA levels for specific genes across cell types in the olfactory epithelium [21]. The vertical axis shows average log2(normalized RNA counts). Each dot represents one cell. The horizontal axis shows cell groups in the pseudotime lineage order determined by Fletcher and colleagues and is summarized at the top of panel A. (A) RNA levels for Rrm2, a gene specific to DNA synthesis in S phase. (B) RNA levels for genes that drive centriole formation Plk4 and Stil. (C) RNA levels for NeuroD1, a transcription factor marking early immediate neuronal precursor cells. Center lines = mean. Error bars = standard deviation. See S2 Data for values. (D-E) Fluorescence images of olfactory epithelium from adult mice expressing eGFP-centrin2 and Arl13b-mCherry. Cryosections were stained with antibodies against NeuroD1 and γ tubulin and with DAPI to mark DNA. (D) A NeuroD1-positive cell with two centrioles. (E) A NeuroD1-positive cell with greater than two centrioles. DNA is excluded from the merge. Scale bars = 5 μm. (F) Comparison of centriole counts in different cell types from olfactory epithelium of adult mice expressing eGFP-centrin2 and Arl13b-mCherry. Centrioles in NeuroD1-positive cells were counted in dissociated olfactory epithelia (N = 2 mice, n = 40 cells). Centrioles in OSNs were counted by en face imaging of the apical surface of septum olfactory epithelia (N = 6 mice, n = 90 cells). Note the small population of NeuroD1-positive cells with unamplified centrioles. See S3 Data for centriole counts. See S3 Fig for additional details. Arl13b-mCherry, ADP-ribosylation-factor-like GTPase 13b; eGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; NeuroD1, neuronal differentiation 1; OSN, olfactory sensory neuron; Plk4, polo-like kinase 4; Rrm2, ribonucleotide reductase molecule 2; Stil, SCL/Tal1 interrupting locus gene.