Fig. 1. Determination of a conserved hinge in DIII of gB.
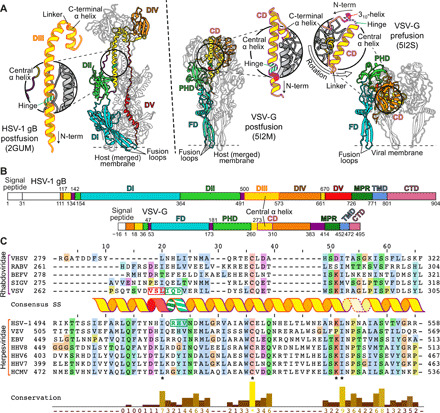
(A) Trimeric ectodomain x-ray structures of gB in postfusion (6) and VSV-G in postfusion (11) and prefusion (12) conformation. Corresponding domains are depicted using the same color scheme for a single protomer. The central helices of each of the protomers are magnified and displayed in insets. The hinge regions in gB RHV515–517 and VSV-G IQD272–274 are marked in striped green and the 310-helix VSL269–271 in red. Location of fusion loops is marked for one protomer. Domains are named according to (6) for gB and (16) for VSV-G. CD, central domain; PHD, pleckstrin homology domain; FD, fusion domain. (B) Domain architecture of gB and VSV-G. Numbers indicate amino acid positions of the domain boundaries. N-terminal signal peptides and the unstructured N-terminal domain of gB are shown in white, and flexible linker regions are shown in purple. CTD, C-terminal domain. (C) Sequence alignment of central helices of glycoprotein G [domain II (DII)] of Rhabdoviridae and glycoprotein B (DIII) of human Herpesviridae. The consensus secondary structure of the central postfusion coiled-coil helix of VSV (11) and HSV-1 (6) is shown in between the alignment of the two virus families. The color outlining the helix indicates the length of the helix of VSV-G (purple) and HSV-1 gB (orange), respectively, while the dashed outline marks the linker region to the C-terminally attached short helix. The residues forming the N-terminal 310-helix of the prefusion VSV-G structure are shown in red letters, and the hinge region residues of the same structure as well as the putative hinge in HSV-1 gB are shown in green letters. Residue background coloring is based on Clustal Omega (39), and conservation was calculated using www.compbio.dundee.ac.uk/aacon/ (40). Three highly conserved, sequence signatures are marked by asterisks on the bottom of the alignment. VHSV: viral hemorrhagic septicaemia virus; RABV: rabies virus; BEFV: bovine ephemeral fever virus; SIGV: Drosophila melanogaster sigma virus; VZV: varicella zoster virus; EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; HHV8: Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus; HHV6: human herpesvirus 6; HHV7: human herpesvirus 7; HCMV: human cytomegalovirus.
