Fig. 3. Locking and functionally arresting the gB prefusion conformation.
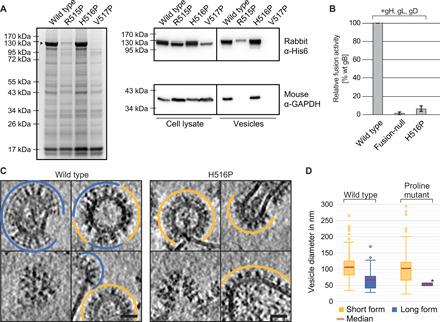
(A) SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and Coomassie stain of extracellular vesicle purifications, obtained from cells transfected with the HSV-1 gB wild type (wt) and single-point mutants, and Western blot analysis of the cell lysate and extracellular vesicles. Mature gB protein is marked by a black arrowhead. Used antibodies are indicated on the right. GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. (B) Fusion activity of gB wt, a fusion-null construct, or a single-point mutant in combination with gH/gL and gD in a cell-cell fusion assay. Activities are normalized to wt fusion activity level. (C) Cryo-ET slices of purified extracellular vesicles formed by WT and gB H516P. The long, postfusion form of gB is indicated by blue lines, and the short form is indicated by orange lines. Lower left images show the top views of gB trimers. Scale bars: 25 nm. (D) Size distribution of vesicles found with short and long gB form on vesicles formed by wt gB (n = 183) and gB H516P (n = 114). Boxes indicate range from first to third quartile with whiskers showing ±1.5 interquartile range and outliers marked as points. *no range given, as only two vesicles were found displaying the long form of gB H516P. The red line marks the median diameter.
