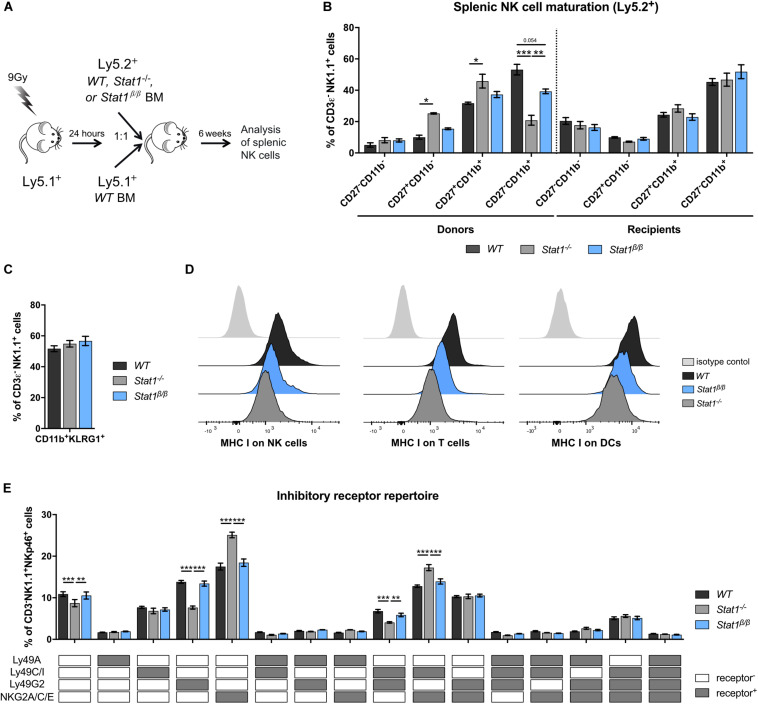
FIGURE 4.
Stat1β/β NK cells exhibit normal maturation in a WT environment and Stat1β/β mice have reduced MHC class I surface levels on various splenocyte types but an unchanged NK cell inhibitory receptor repertoire. (A) Scheme illustrating the mixed bone marrow chimera experiments. (B,C) Splenocytes from donor and bone marrow chimeric mice (Ly5.2+) were analyzed for the NK cell (CD3ε–NK1.1+) maturation subsets CD27–CD11b–, CD27+CD11b–, CD27+CD11b+, and CD27–CD11b+ (B) and for CD11b+KLRG1+ cells (C). (D) Surface levels of MHC class I molecules (MHC I) on splenic NK cells (left), T cells (middle) and DCs (right) from WT, Stat1–/– and Stat1β/β mice were determined by flow cytometry. Histograms show one representative sample per cell type and genotype and the isotype control, which was comparable for cells from mice of all genotypes. (E) The inhibitory receptor repertoire of splenic NK cells (CD3ε–NK1.1+) from WT, Stat1–/–, and Stat1β/β mice was determined by flow cytometry. NK subsets were defined by combinatorial expression of Ly49A, Ly49C/I, Ly49G2, and NKG2A, as determined by flow cytometry, and analyzed by Boolean gating. White and gray boxes indicate whether the population is positive (gray) or negative (white) for the inhibitory receptors listed. Mean percentages ± SEM from three (n = 5–8) (B,C) and two (n = 5–6) (E) experiments are shown. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.